Markov subsampling based Huber Criterion
Paper and Code
Dec 12, 2021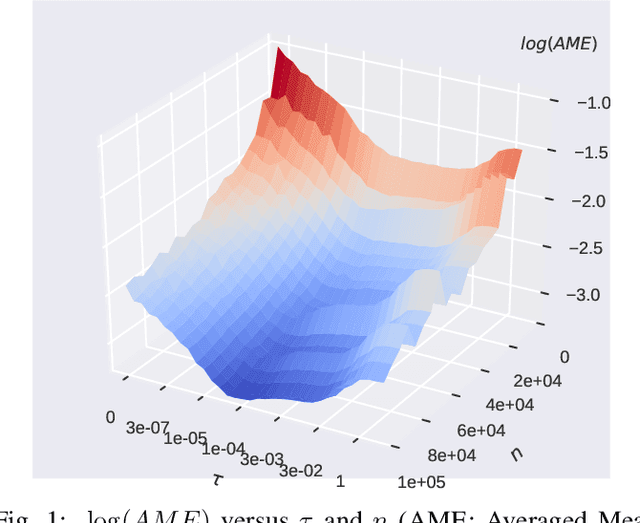
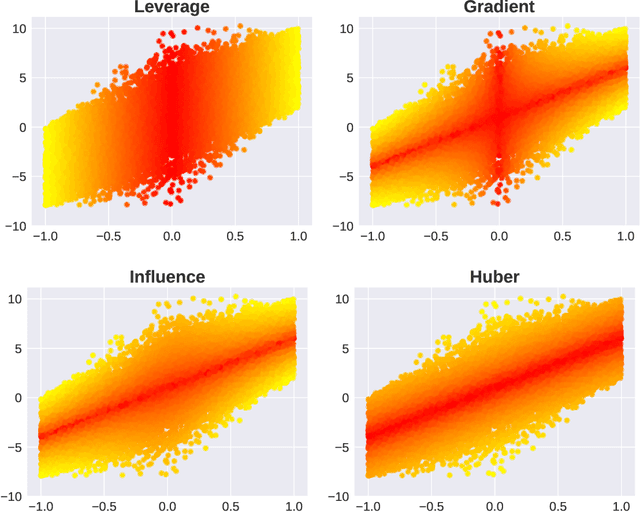
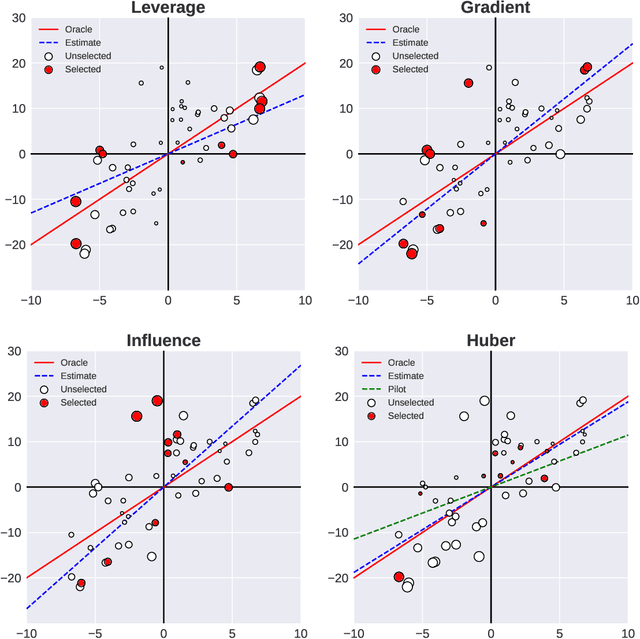
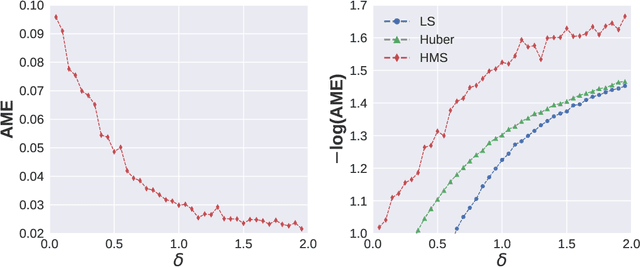
Subsampling is an important technique to tackle the computational challenges brought by big data. Many subsampling procedures fall within the framework of importance sampling, which assigns high sampling probabilities to the samples appearing to have big impacts. When the noise level is high, those sampling procedures tend to pick many outliers and thus often do not perform satisfactorily in practice. To tackle this issue, we design a new Markov subsampling strategy based on Huber criterion (HMS) to construct an informative subset from the noisy full data; the constructed subset then serves as a refined working data for efficient processing. HMS is built upon a Metropolis-Hasting procedure, where the inclusion probability of each sampling unit is determined using the Huber criterion to prevent over scoring the outliers. Under mild conditions, we show that the estimator based on the subsamples selected by HMS is statistically consistent with a sub-Gaussian deviation bound. The promising performance of HMS is demonstrated by extensive studies on large scale simulations and real data examples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge