Market Making with Scaled Beta Policies
Paper and Code
Jul 09, 2022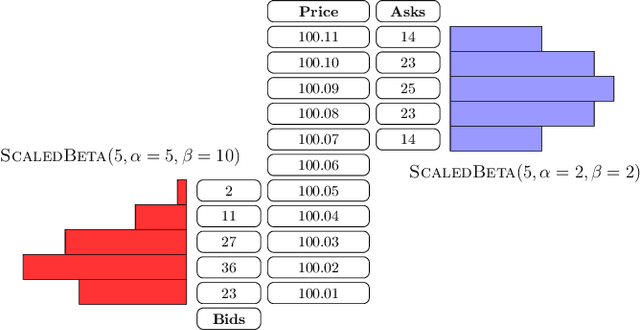
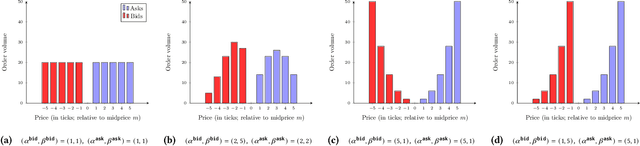
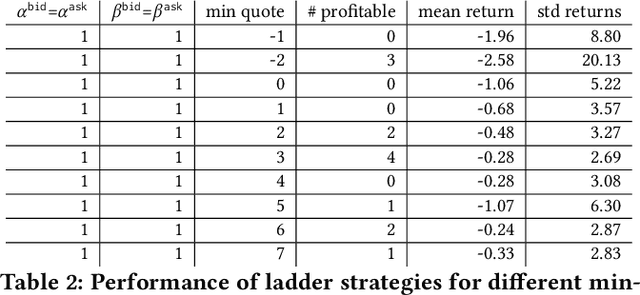
This paper introduces a new representation for the actions of a market maker in an order-driven market. This representation uses scaled beta distributions, and generalises three approaches taken in the artificial intelligence for market making literature: single price-level selection, ladder strategies and "market making at the touch". Ladder strategies place uniform volume across an interval of contiguous prices. Scaled beta distribution based policies generalise these, allowing volume to be skewed across the price interval. We demonstrate that this flexibility is useful for inventory management, one of the key challenges faced by a market maker. In this paper, we conduct three main experiments: first, we compare our more flexible beta-based actions with the special case of ladder strategies; then, we investigate the performance of simple fixed distributions; and finally, we devise and evaluate a simple and intuitive dynamic control policy that adjusts actions in a continuous manner depending on the signed inventory that the market maker has acquired. All empirical evaluations use a high-fidelity limit order book simulator based on historical data with 50 levels on each side.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge