MANTIS: Model-Augmented Neural neTwork with Incoherent k-space Sampling for efficient MR T2 mapping
Paper and Code
Sep 02, 2018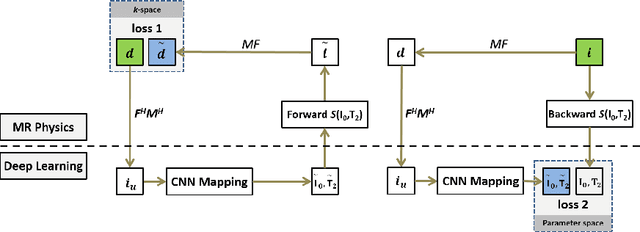

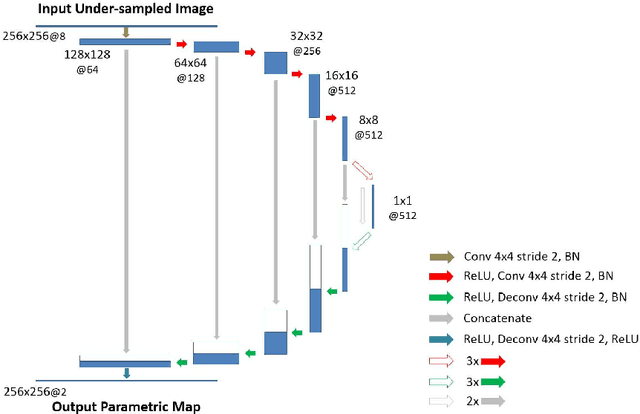

Quantitative mapping of magnetic resonance (MR) parameters have been shown as valuable methods for improved assessment of a range of diseases. Due to the need to image an anatomic structure multiple times, parameter mapping usually requires long scan times compared to conventional static imaging. Therefore, accelerated parameter mapping is highly-desirable and remains a topic of great interest in the MR research community. While many recent deep learning methods have focused on highly efficient image reconstruction for conventional static MR imaging, applications of deep learning for dynamic imaging and in particular accelerated parameter mapping have been limited. The purpose of this work was to develop and evaluate a novel deep learning-based reconstruction framework called Model-Augmented Neural neTwork with Incoherent k-space Sampling (MANTIS) for efficient MR parameter mapping. Our approach combines end-to-end CNN mapping with k-space consistency using the concept of cyclic loss to further enforce data and model fidelity. Incoherent k-space sampling is used to improve reconstruction performance. A physical model is incorporated into the proposed framework, so that the parameter maps can be efficiently estimated directly from undersampled images. The performance of MANTIS was demonstrated for the spin-spin relaxation time (T2) mapping of the knee joint. Compared to conventional reconstruction approaches that exploited image sparsity, MANTIS yielded lower errors and higher similarity with respect to the reference in the T2 estimation. Our study demonstrated that the proposed MANTIS framework, with a combination of end-to-end CNN mapping, signal model-augmented data consistency, and incoherent k-space sampling, represents a promising approach for efficient MR parameter mapping. MANTIS can potentially be extended to other types of parameter mapping with appropriate models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge