Manifold Optimization for High Accuracy Spatial Location Estimation Using Ultrasound Waves
Paper and Code
Mar 28, 2021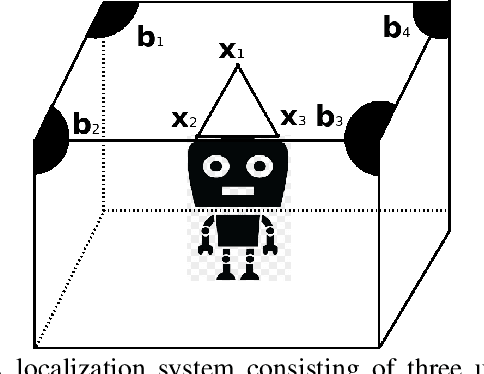
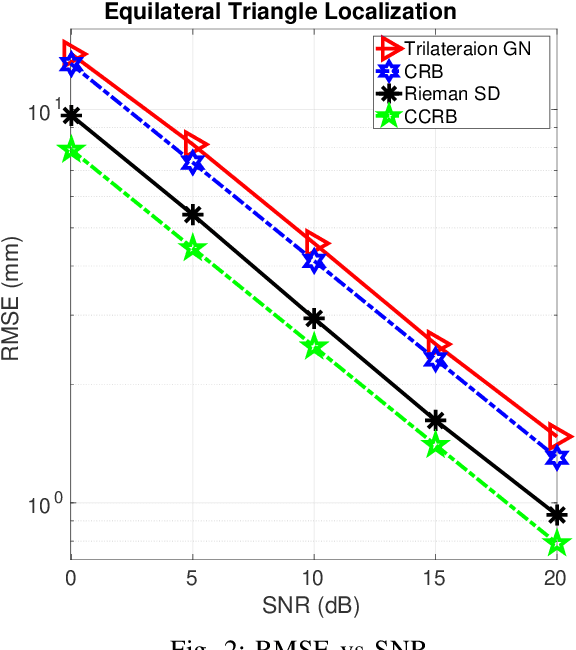
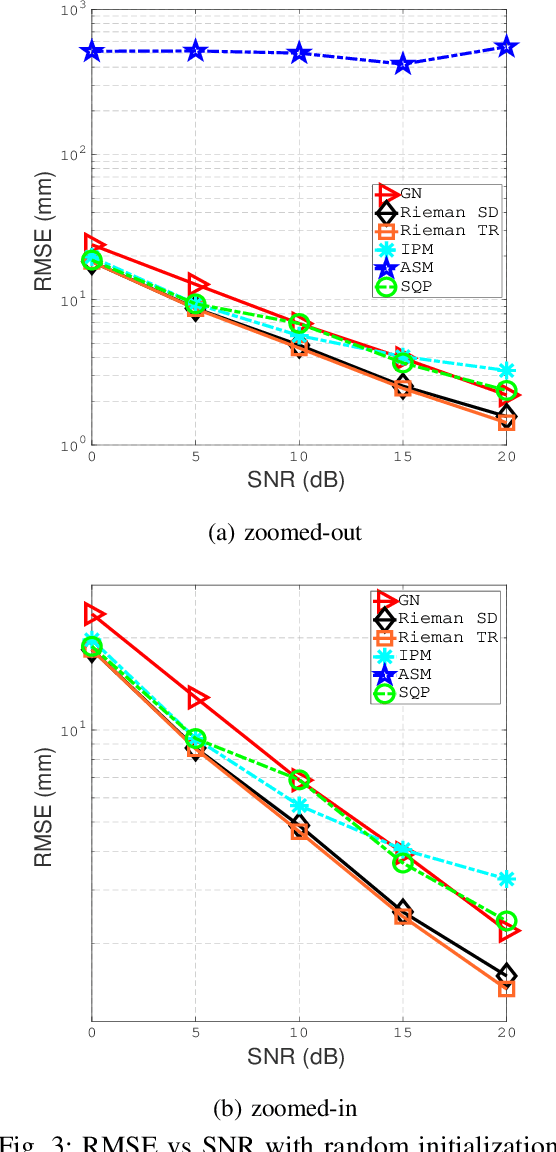
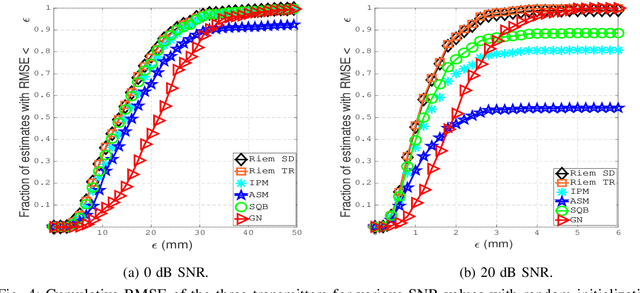
This paper designs a high accuracy spatial location estimation method using ultrasound waves by exploiting the fixed geometry of the transmitters. Assuming an equilateral triangle antenna configuration, where three antennas are placed as the vertices of an equilateral triangle, the spatial location problem can be formulated as a non-convex optimization problem whose interior is shown to admit a Riemannian manifold structure. The investigation of the geometry of the newly introduced manifold, i.e. the manifold of all equilateral triangles in R^3, allows the design of highly efficient optimization algorithms. Simulation results are presented to compare the performance of the proposed approach against popular methods from the literature. The results suggest that the proposed Riemannian-based methods outperform the state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, the proposed Riemannian methods require much smaller computation time as compared with popular generic non-convex approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge