Machine Translation Evaluation Benchmark for Wu Chinese: Workflow and Analysis
Paper and Code
Oct 14, 2024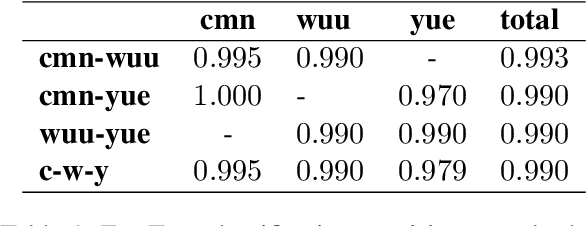
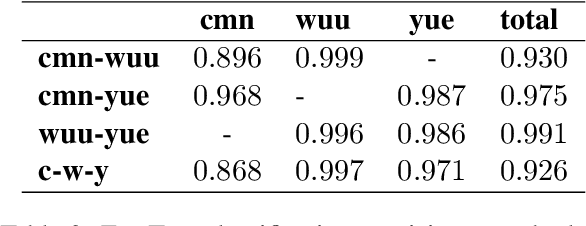
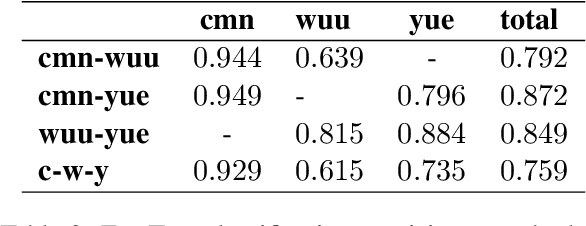
We introduce a FLORES+ dataset as an evaluation benchmark for modern Wu Chinese machine translation models and showcase its compatibility with existing Wu data. Wu Chinese is mutually unintelligible with other Sinitic languages such as Mandarin and Yue (Cantonese), but uses a set of Hanzi (Chinese characters) that profoundly overlaps with others. The population of Wu speakers is the second largest among languages in China, but the language has been suffering from significant drop in usage especially among the younger generations. We identify Wu Chinese as a textually low-resource language and address challenges for its machine translation models. Our contributions include: (1) an open-source, manually translated dataset, (2) full documentations on the process of dataset creation and validation experiments, (3) preliminary tools for Wu Chinese normalization and segmentation, and (4) benefits and limitations of our dataset, as well as implications to other low-resource languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge