Machine Learning on Dynamic Functional Connectivity: Promise, Pitfalls, and Interpretations
Paper and Code
Sep 17, 2024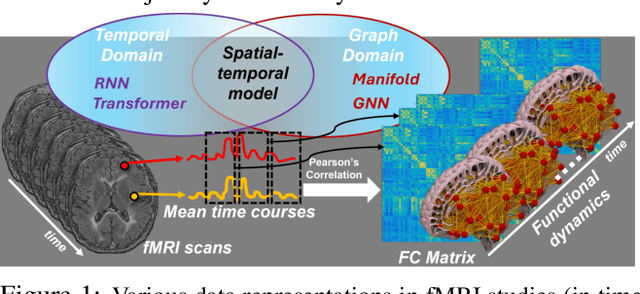
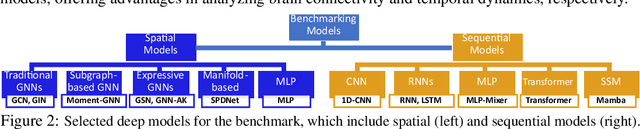
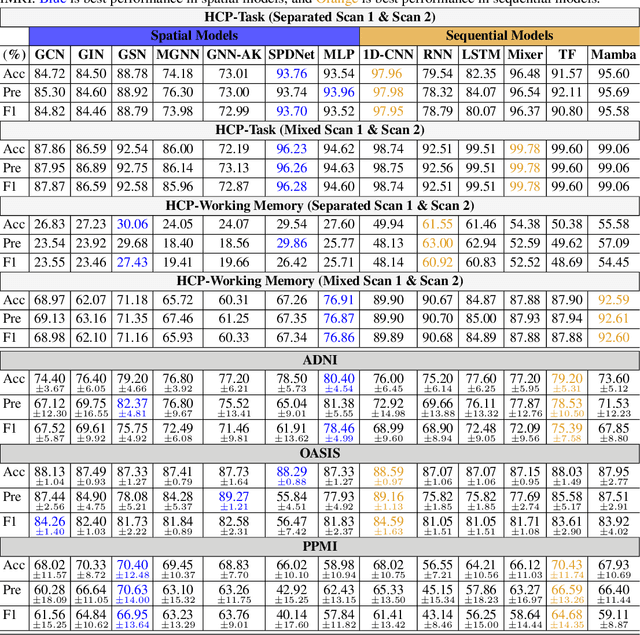
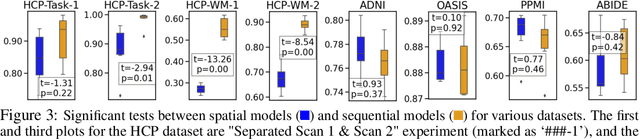
An unprecedented amount of existing functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) data provides a new opportunity to understand the relationship between functional fluctuation and human cognition/behavior using a data-driven approach. To that end, tremendous efforts have been made in machine learning to predict cognitive states from evolving volumetric images of blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signals. Due to the complex nature of brain function, however, the evaluation on learning performance and discoveries are not often consistent across current state-of-the-arts (SOTA). By capitalizing on large-scale existing neuroimaging data (34,887 data samples from six public databases), we seek to establish a well-founded empirical guideline for designing deep models for functional neuroimages by linking the methodology underpinning with knowledge from the neuroscience domain. Specifically, we put the spotlight on (1) What is the current SOTA performance in cognitive task recognition and disease diagnosis using fMRI? (2) What are the limitations of current deep models? and (3) What is the general guideline for selecting the suitable machine learning backbone for new neuroimaging applications? We have conducted a comprehensive evaluation and statistical analysis, in various settings, to answer the above outstanding questions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge