M2MRF: Many-to-Many Reassembly of Features for Tiny Lesion Segmentation in Fundus Images
Paper and Code
Oct 30, 2021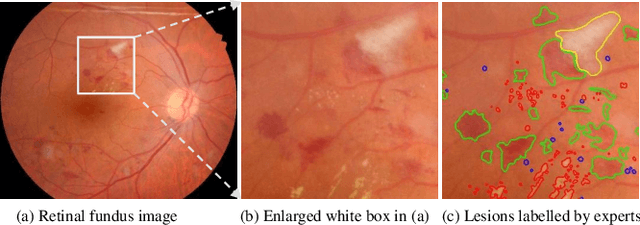
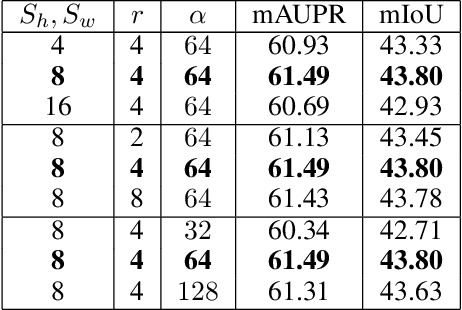
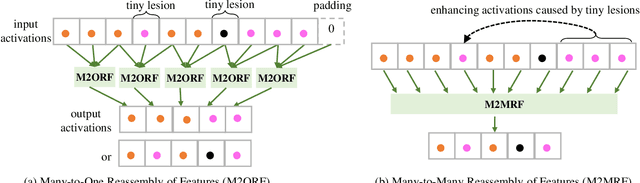
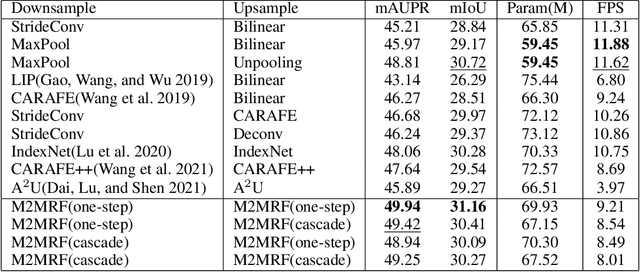
Feature reassembly is an essential component in modern CNNs-based segmentation approaches, which includes feature downsampling and upsampling operators. Existing feature reassembly operators reassemble multiple features from a small predefined region into one for each target location independently. This may result in loss of spatial information, which could vanish activations of tiny lesions particularly when they cluster together. In this paper, we propose a many-to-many reassembly of features (M2MRF). It reassembles features in a dimension-reduced feature space and simultaneously aggregates multiple features inside a large predefined region into multiple target features. In this way, long range spatial dependencies are captured to maintain activations on tiny lesions, particularly when multiple lesions coexist. Experimental results on two lesion segmentation benchmarks, i.e. DDR and IDRiD, show that our M2MRF outperforms existing feature reassembly operators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge