LUNAR: Unifying Local Outlier Detection Methods via Graph Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Dec 10, 2021
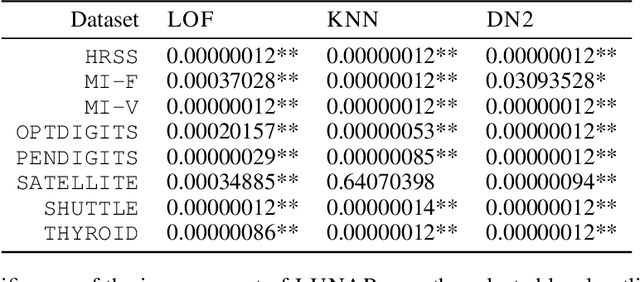
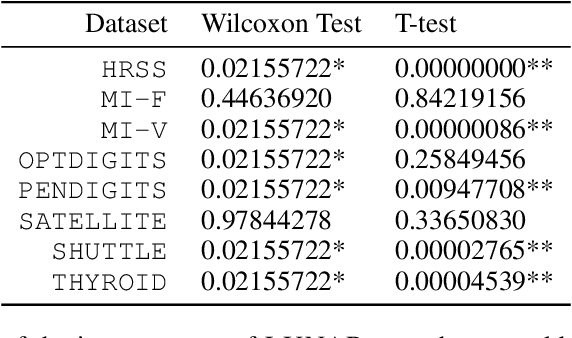
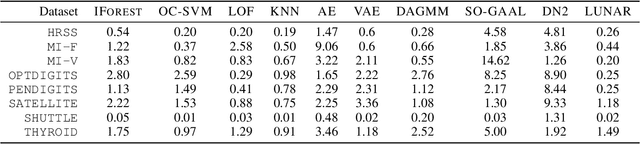
Many well-established anomaly detection methods use the distance of a sample to those in its local neighbourhood: so-called `local outlier methods', such as LOF and DBSCAN. They are popular for their simple principles and strong performance on unstructured, feature-based data that is commonplace in many practical applications. However, they cannot learn to adapt for a particular set of data due to their lack of trainable parameters. In this paper, we begin by unifying local outlier methods by showing that they are particular cases of the more general message passing framework used in graph neural networks. This allows us to introduce learnability into local outlier methods, in the form of a neural network, for greater flexibility and expressivity: specifically, we propose LUNAR, a novel, graph neural network-based anomaly detection method. LUNAR learns to use information from the nearest neighbours of each node in a trainable way to find anomalies. We show that our method performs significantly better than existing local outlier methods, as well as state-of-the-art deep baselines. We also show that the performance of our method is much more robust to different settings of the local neighbourhood size.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge