LoRTA: Low Rank Tensor Adaptation of Large Language Models
Paper and Code
Oct 15, 2024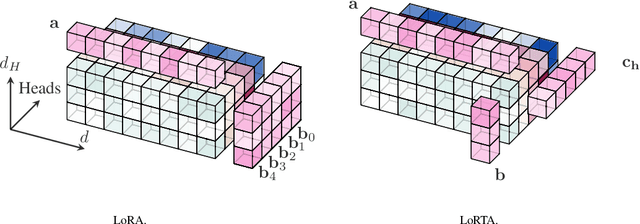

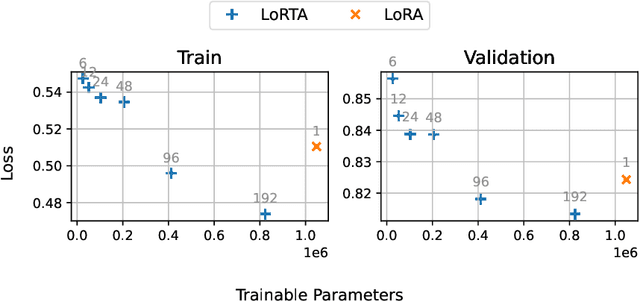

Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is a popular Parameter Efficient Fine Tuning (PEFT) method that effectively adapts large pre-trained models for downstream tasks. LoRA parameterizes model updates using low-rank matrices at each layer, significantly reducing the number of trainable parameters and, consequently, resource requirements during fine-tuning. However, the lower bound on the number of trainable parameters remains high due to the use of the low-rank matrix model. In this paper, we address this limitation by proposing a novel approach that employs a low rank tensor parametrization for model updates. The proposed low rank tensor model can significantly reduce the number of trainable parameters, while also allowing for finer-grained control over adapter size. Our experiments on Natural Language Understanding, Instruction Tuning, Preference Optimization and Protein Folding benchmarks demonstrate that our method is both efficient and effective for fine-tuning large language models, achieving a substantial reduction in the number of parameters while maintaining comparable performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge