LiDAR Aided Future Beam Prediction in Real-World Millimeter Wave V2I Communications
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2022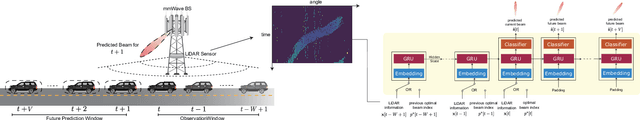

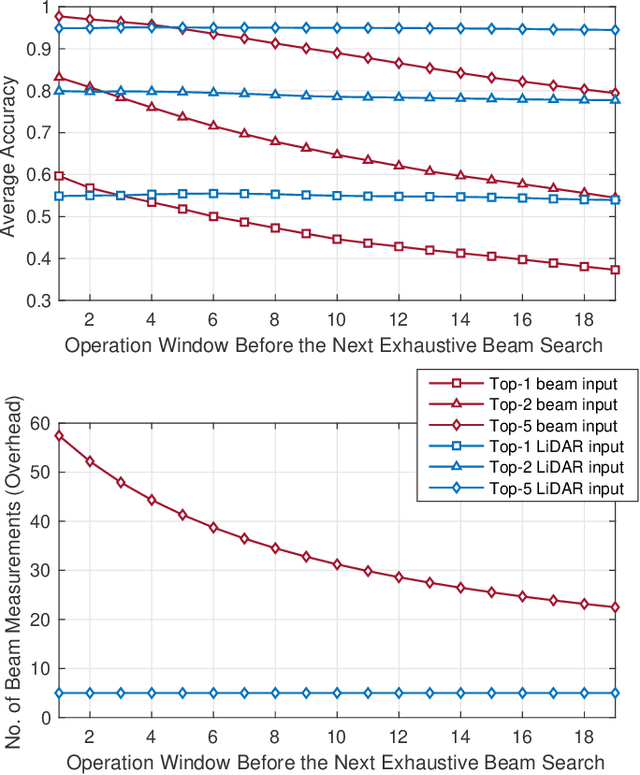
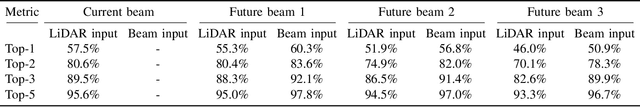
This paper presents the first large-scale real-world evaluation for using LiDAR data to guide the mmWave beam prediction task. A machine learning (ML) model that leverages the LiDAR sensory data to predict the current and future beams was developed. Based on the large-scale real-world dataset, DeepSense 6G, this model was evaluated in a vehicle-to-infrastructure communication scenario with highly-mobile vehicles. The experimental results show that the developed LiDAR-aided beam prediction and tracking model can predict the optimal beam in $95\%$ of the cases and with more than $90\%$ reduction in the beam training overhead. The LiDAR-aided beam tracking achieves comparable accuracy performance to a baseline solution that has perfect knowledge of the previous optimal beams, without requiring any knowledge about the previous optimal beam information and without any need for beam calibration. This highlights a promising solution for the critical beam alignment challenges in mmWave and terahertz communication systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge