Lexical Co-occurrence, Statistical Significance, and Word Association
Paper and Code
Aug 31, 2010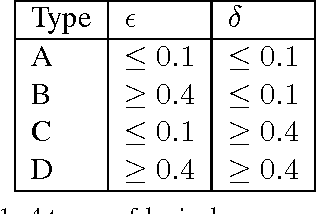
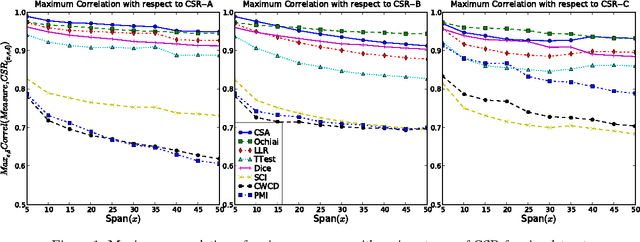
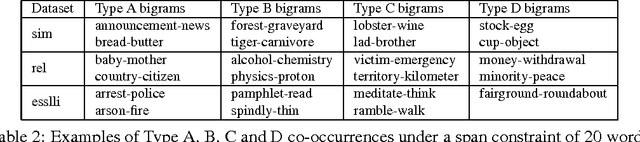
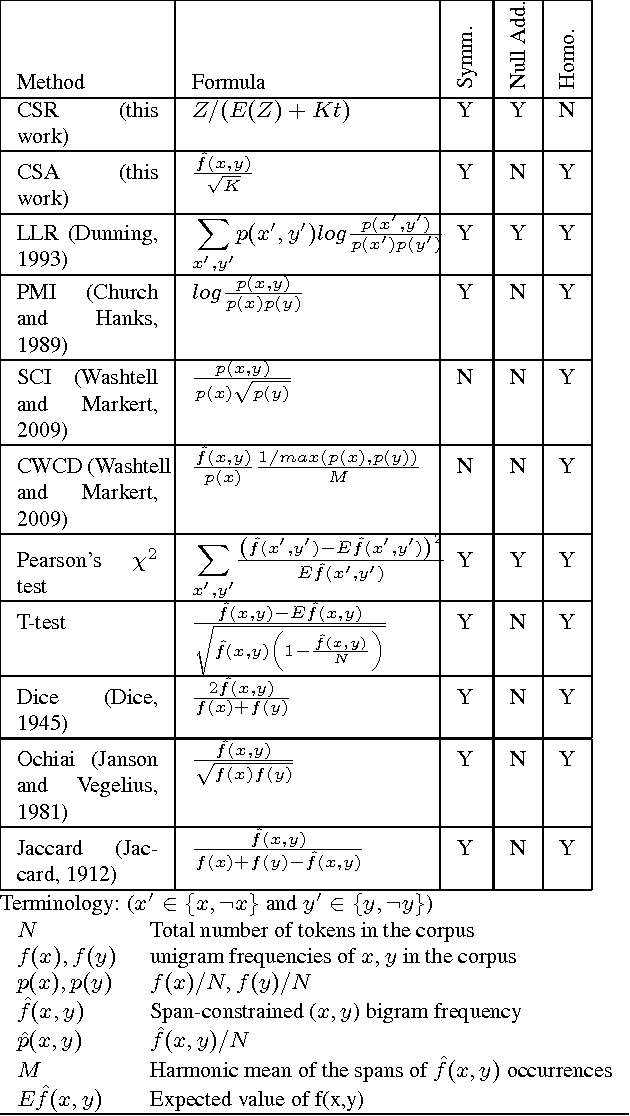
Lexical co-occurrence is an important cue for detecting word associations. We present a theoretical framework for discovering statistically significant lexical co-occurrences from a given corpus. In contrast with the prevalent practice of giving weightage to unigram frequencies, we focus only on the documents containing both the terms (of a candidate bigram). We detect biases in span distributions of associated words, while being agnostic to variations in global unigram frequencies. Our framework has the fidelity to distinguish different classes of lexical co-occurrences, based on strengths of the document and corpuslevel cues of co-occurrence in the data. We perform extensive experiments on benchmark data sets to study the performance of various co-occurrence measures that are currently known in literature. We find that a relatively obscure measure called Ochiai, and a newly introduced measure CSA capture the notion of lexical co-occurrence best, followed next by LLR, Dice, and TTest, while another popular measure, PMI, suprisingly, performs poorly in the context of lexical co-occurrence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge