Leveraging Explainable AI for LLM Text Attribution: Differentiating Human-Written and Multiple LLMs-Generated Text
Paper and Code
Jan 06, 2025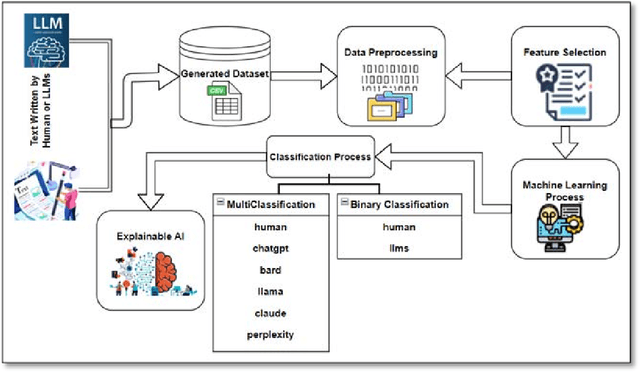
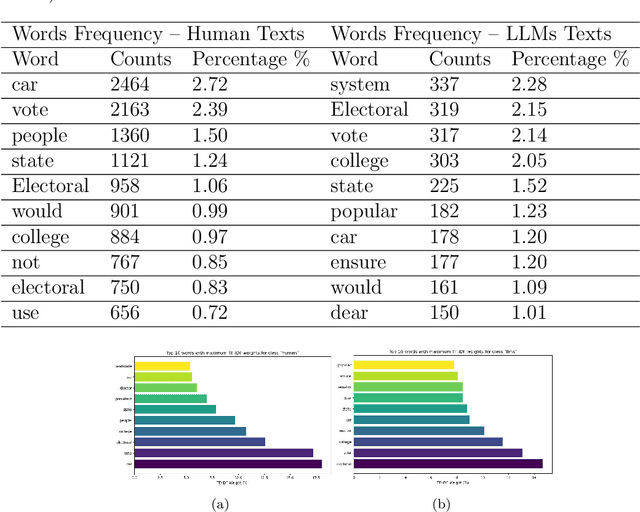
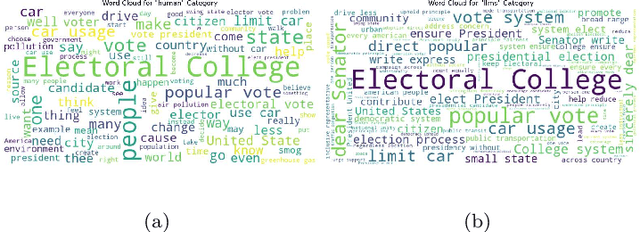
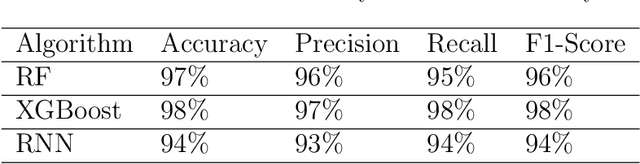
The development of Generative AI Large Language Models (LLMs) raised the alarm regarding identifying content produced through generative AI or humans. In one case, issues arise when students heavily rely on such tools in a manner that can affect the development of their writing or coding skills. Other issues of plagiarism also apply. This study aims to support efforts to detect and identify textual content generated using LLM tools. We hypothesize that LLMs-generated text is detectable by machine learning (ML), and investigate ML models that can recognize and differentiate texts generated by multiple LLMs tools. We leverage several ML and Deep Learning (DL) algorithms such as Random Forest (RF), and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), and utilized Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) to understand the important features in attribution. Our method is divided into 1) binary classification to differentiate between human-written and AI-text, and 2) multi classification, to differentiate between human-written text and the text generated by the five different LLM tools (ChatGPT, LLaMA, Google Bard, Claude, and Perplexity). Results show high accuracy in the multi and binary classification. Our model outperformed GPTZero with 98.5\% accuracy to 78.3\%. Notably, GPTZero was unable to recognize about 4.2\% of the observations, but our model was able to recognize the complete test dataset. XAI results showed that understanding feature importance across different classes enables detailed author/source profiles. Further, aiding in attribution and supporting plagiarism detection by highlighting unique stylistic and structural elements ensuring robust content originality verification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge