Learning structures of the French clinical language:development and validation of word embedding models using 21 million clinical reports from electronic health records
Paper and Code
Jul 26, 2022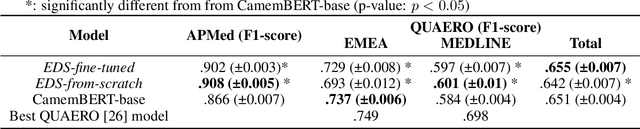
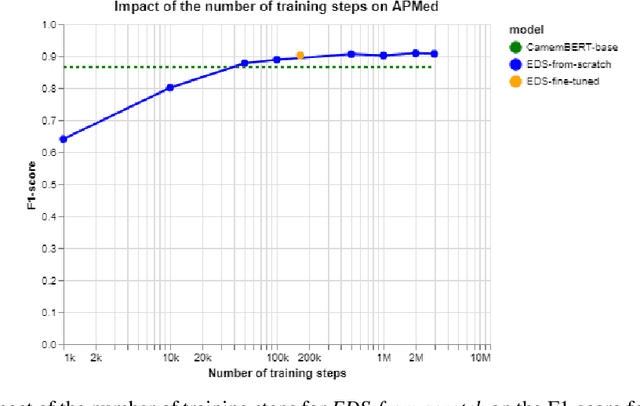
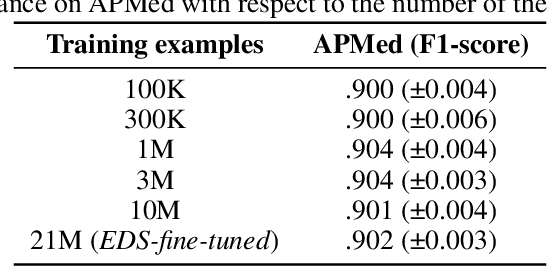
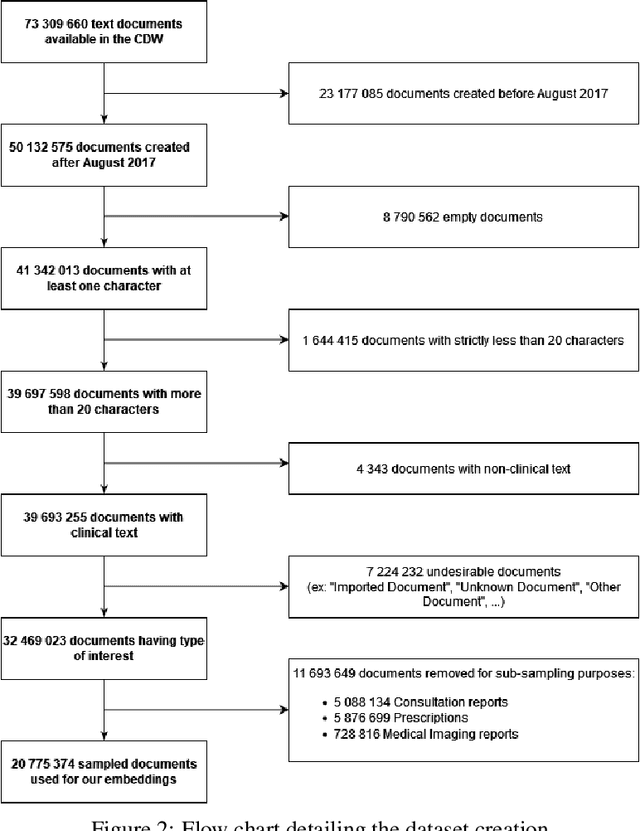
Background Clinical studies using real-world data may benefit from exploiting clinical reports, a particularly rich albeit unstructured medium. To that end, natural language processing can extract relevant information. Methods based on transfer learning using pre-trained language models have achieved state-of-the-art results in most NLP applications; however, publicly available models lack exposure to speciality-languages, especially in the medical field. Objective We aimed to evaluate the impact of adapting a language model to French clinical reports on downstream medical NLP tasks. Methods We leveraged a corpus of 21M clinical reports collected from August 2017 to July 2021 at the Greater Paris University Hospitals (APHP) to produce two CamemBERT architectures on speciality language: one retrained from scratch and the other using CamemBERT as its initialisation. We used two French annotated medical datasets to compare our language models to the original CamemBERT network, evaluating the statistical significance of improvement with the Wilcoxon test. Results Our models pretrained on clinical reports increased the average F1-score on APMed (an APHP-specific task) by 3 percentage points to 91%, a statistically significant improvement. They also achieved performance comparable to the original CamemBERT on QUAERO. These results hold true for the fine-tuned and from-scratch versions alike, starting from very few pre-training samples. Conclusions We confirm previous literature showing that adapting generalist pre-train language models such as CamenBERT on speciality corpora improves their performance for downstream clinical NLP tasks. Our results suggest that retraining from scratch does not induce a statistically significant performance gain compared to fine-tuning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge