Learning Sparse Interaction Graphs of Partially Observed Pedestrians for Trajectory Prediction
Paper and Code
Jul 19, 2021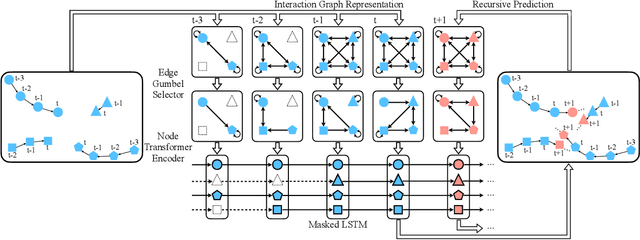
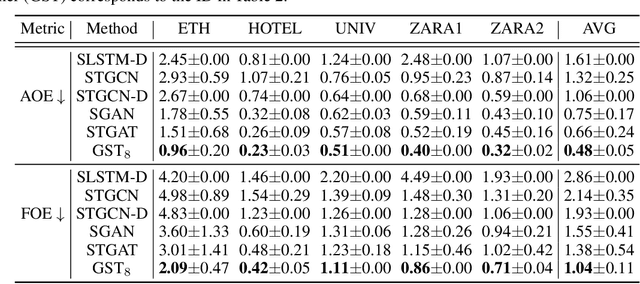
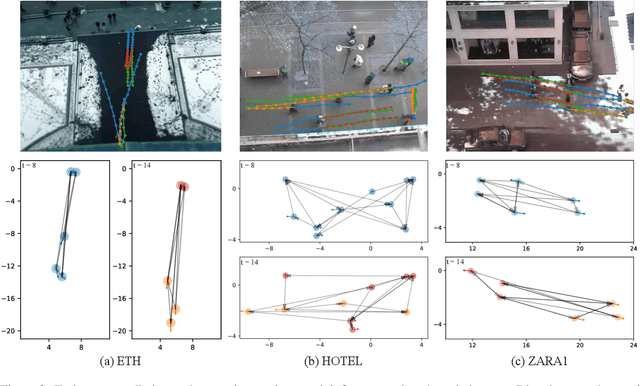
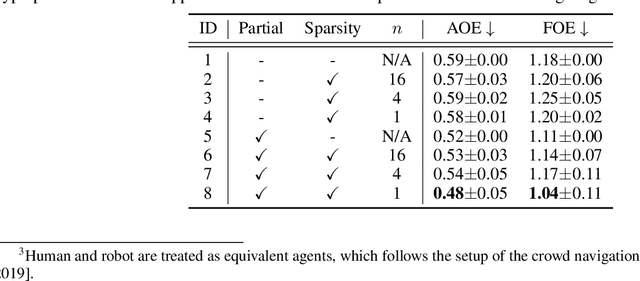
Multi-pedestrian trajectory prediction is an indispensable safety element of autonomous systems that interact with crowds in unstructured environments. Many recent efforts have developed trajectory prediction algorithms with focus on understanding social norms behind pedestrian motions. Yet we observe these works usually hold two assumptions that prevent them from being smoothly applied to robot applications: positions of all pedestrians are consistently tracked; the target agent pays attention to all pedestrians in the scene. The first assumption leads to biased interaction modeling with incomplete pedestrian data, and the second assumption introduces unnecessary disturbances and leads to the freezing robot problem. Thus, we propose Gumbel Social Transformer, in which an Edge Gumbel Selector samples a sparse interaction graph of partially observed pedestrians at each time step. A Node Transformer Encoder and a Masked LSTM encode the pedestrian features with the sampled sparse graphs to predict trajectories. We demonstrate that our model overcomes the potential problems caused by the assumptions, and our approach outperforms the related works in benchmark evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge