Learning Sparse Graphon Mean Field Games
Paper and Code
Sep 08, 2022
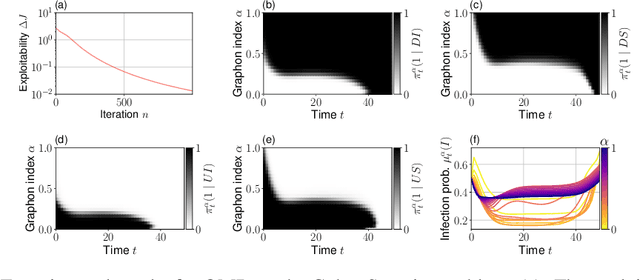
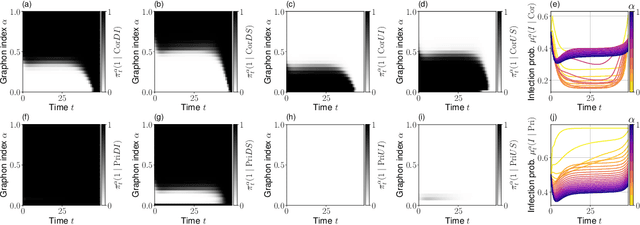

Although the field of multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) has made considerable progress in the last years, solving systems with a large number of agents remains a hard challenge. Graphon mean field games (GMFGs) enable the scalable analysis of MARL problems that are otherwise intractable. By the mathematical structure of graphons, this approach is limited to dense graphs which are insufficient to describe many real-world networks such as power law graphs. Our paper introduces a novel formulation of GMFGs, called LPGMFGs, which leverages the graph theoretical concept of $L^p$ graphons and provides a machine learning tool to efficiently and accurately approximate solutions for sparse network problems. This especially includes power law networks which are empirically observed in various application areas and cannot be captured by standard graphons. We derive theoretical existence and convergence guarantees and give empirical examples that demonstrate the accuracy of our learning approach for systems with many agents. Furthermore, we rigorously extend the Online Mirror Descent (OMD) learning algorithm to our setup to accelerate learning speed, allow for agent interaction through the mean field in the transition kernel, and empirically show its capabilities. In general, we provide a scalable, mathematically well-founded machine learning approach to a large class of otherwise intractable problems of great relevance in numerous research fields.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge