Learning Neural Hamiltonian Dynamics: A Methodological Overview
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2022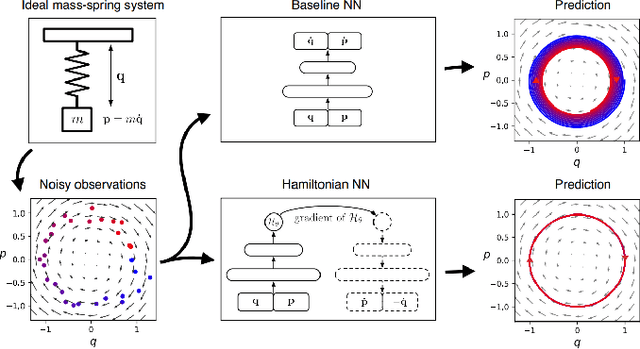
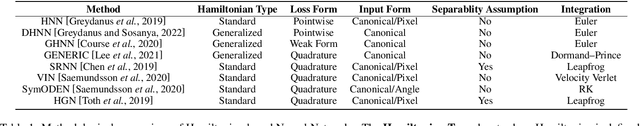
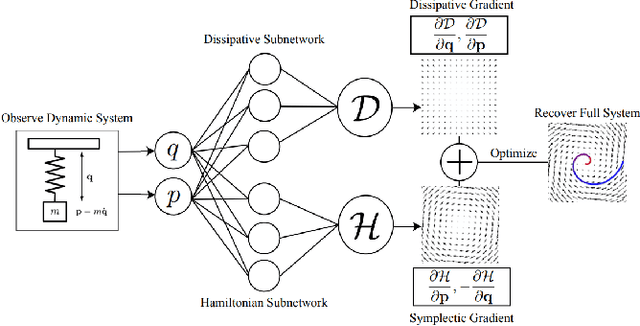
The past few years have witnessed an increased interest in learning Hamiltonian dynamics in deep learning frameworks. As an inductive bias based on physical laws, Hamiltonian dynamics endow neural networks with accurate long-term prediction, interpretability, and data-efficient learning. However, Hamiltonian dynamics also bring energy conservation or dissipation assumptions on the input data and additional computational overhead. In this paper, we systematically survey recently proposed Hamiltonian neural network models, with a special emphasis on methodologies. In general, we discuss the major contributions of these models, and compare them in four overlapping directions: 1) generalized Hamiltonian system; 2) symplectic integration, 3) generalized input form, and 4) extended problem settings. We also provide an outlook of the fundamental challenges and emerging opportunities in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge