Learning Implicit Priors for Motion Optimization
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2022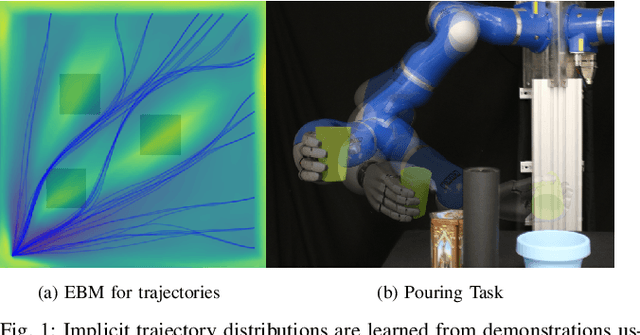
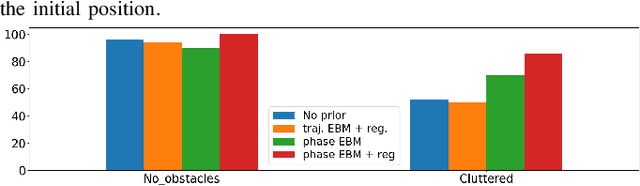
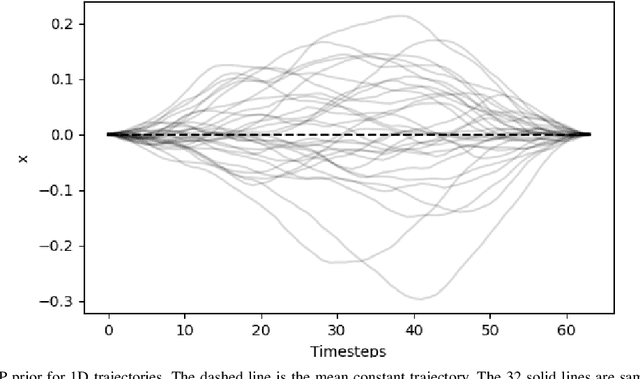
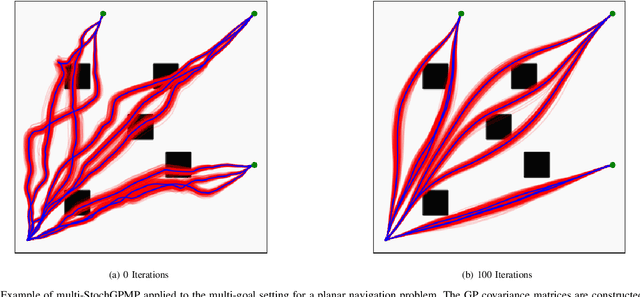
In this paper, we focus on the problem of integrating Energy-based Models (EBM) as guiding priors for motion optimization. EBMs are a set of neural networks that can represent expressive probability density distributions in terms of a Gibbs distribution parameterized by a suitable energy function. Due to their implicit nature, they can easily be integrated as optimization factors or as initial sampling distributions in the motion optimization problem, making them good candidates to integrate data-driven priors in the motion optimization problem. In this work, we present a set of required modeling and algorithmic choices to adapt EBMs into motion optimization. We investigate the benefit of including additional regularizers in the learning of the EBMs to use them with gradient-based optimizers and we present a set of EBM architectures to learn generalizable distributions for manipulation tasks. We present multiple cases in which the EBM could be integrated for motion optimization and evaluate the performance of learned EBMs as guiding priors for both simulated and real robot experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge