Learning Human-like Hand Reaching for Human-Robot Handshaking
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2021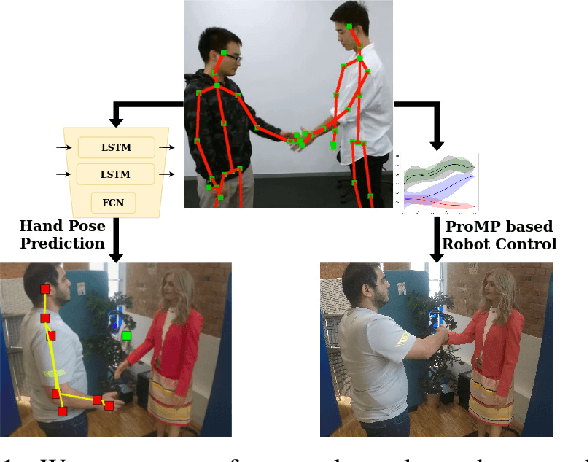
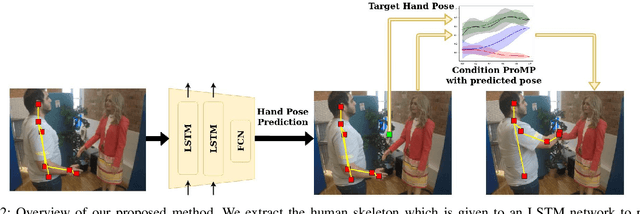
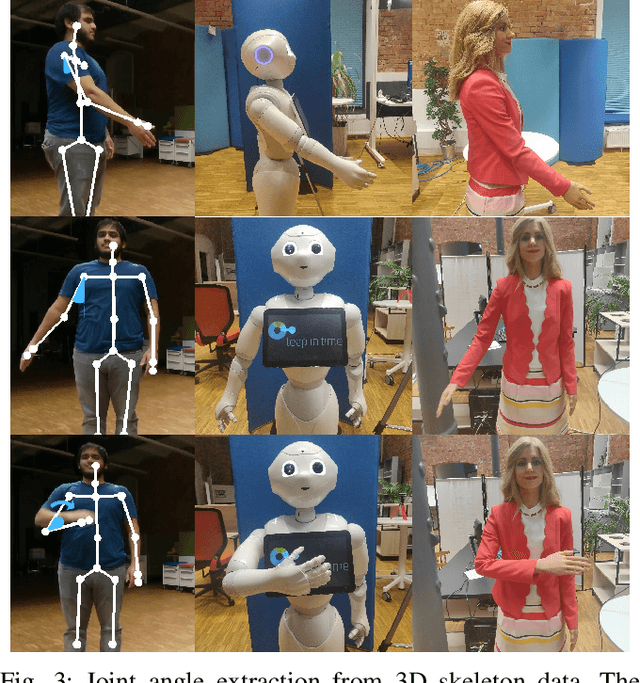
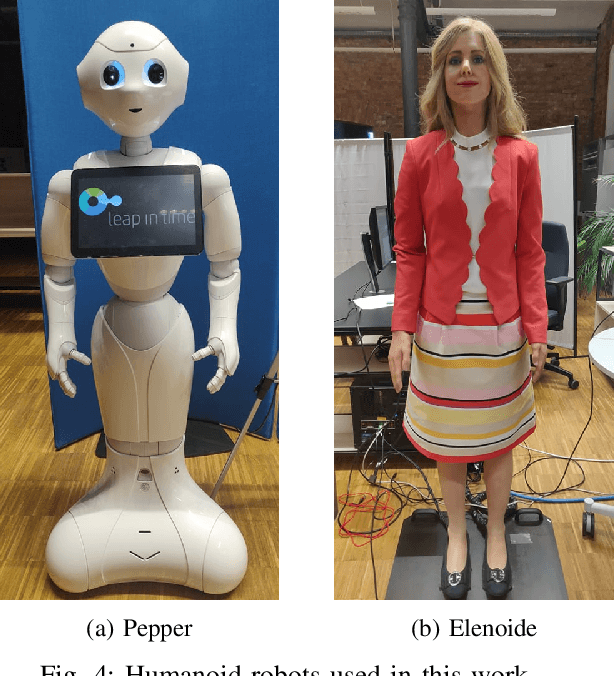
One of the first and foremost non-verbal interactions that humans perform is a handshake. It has an impact on first impressions as touch can convey complex emotions. This makes handshaking an important skill for the repertoire of a social robot. In this paper, we present a novel framework for learning human-robot handshaking behaviours for humanoid robots solely using third-person human-human interaction data. This is especially useful for non-backdrivable robots that cannot be taught by demonstrations via kinesthetic teaching. Our approach can be easily executed on different humanoid robots. This removes the need for re-training, which is especially tedious when training with human-interaction partners. We show this by applying the learnt behaviours on two different humanoid robots with similar degrees of freedom but different shapes and control limits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge