Learning from Incremental Directional Corrections
Paper and Code
Nov 30, 2020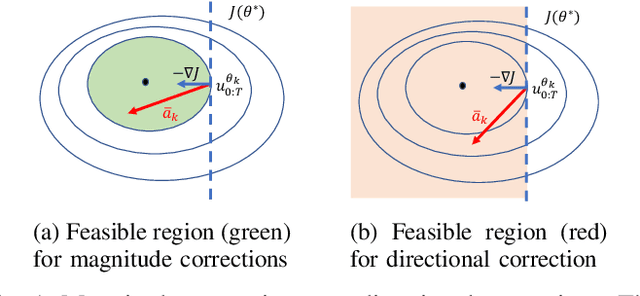
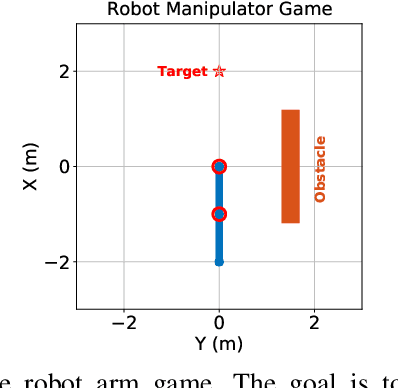
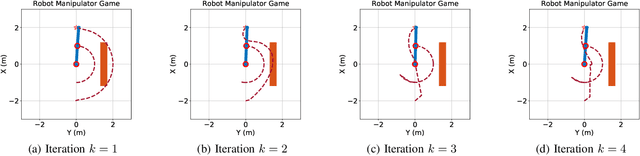
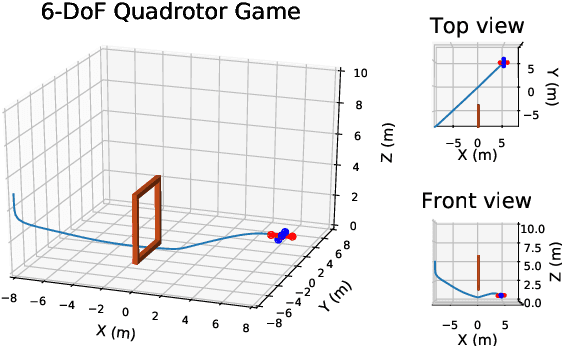
This paper proposes a technique which enables a robot to learn a control objective function incrementally from human user's corrections. The human's corrections can be as simple as directional corrections -- corrections that indicate the direction of a control change without indicating its magnitude -- applied at some time instances during the robot's motion. We only assume that each of the human's corrections, regardless of its magnitude, points in a direction that improves the robot's current motion relative to an implicit objective function. The proposed method uses the direction of a correction to update the estimate of the objective function based on a cutting plane technique. We establish the theoretical results to show that this process of incremental correction and update guarantees convergence of the learned objective function to the implicit one. The method is validated by both simulations and two human-robot games, where human players teach a 2-link robot arm and a 6-DoF quadrotor system for motion planning in environments with obstacles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge