Learning Compositional Representations for Effective Low-Shot Generalization
Paper and Code
Apr 17, 2022
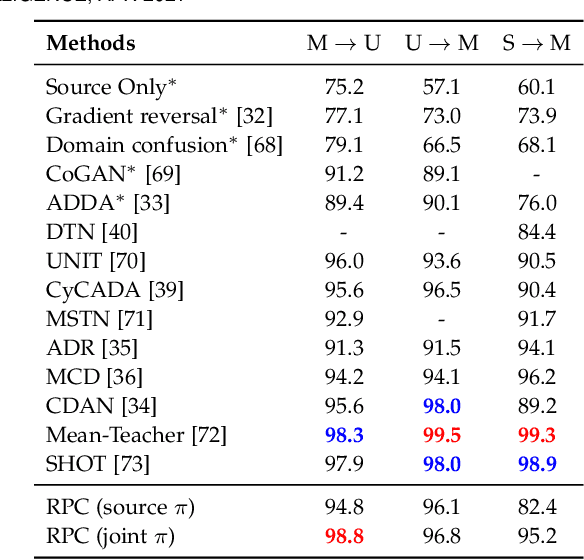
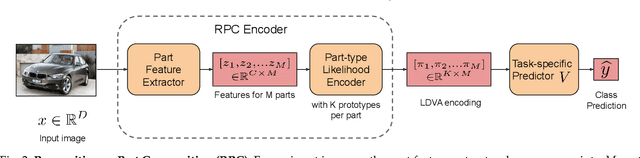
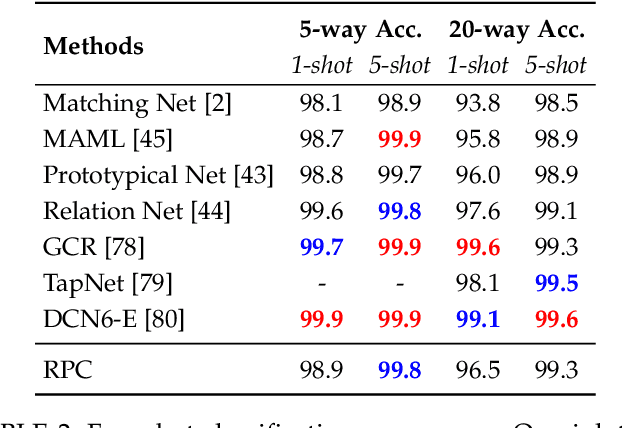
We propose Recognition as Part Composition (RPC), an image encoding approach inspired by human cognition. It is based on the cognitive theory that humans recognize complex objects by components, and that they build a small compact vocabulary of concepts to represent each instance with. RPC encodes images by first decomposing them into salient parts, and then encoding each part as a mixture of a small number of prototypes, each representing a certain concept. We find that this type of learning inspired by human cognition can overcome hurdles faced by deep convolutional networks in low-shot generalization tasks, like zero-shot learning, few-shot learning and unsupervised domain adaptation. Furthermore, we find a classifier using an RPC image encoder is fairly robust to adversarial attacks, that deep neural networks are known to be prone to. Given that our image encoding principle is based on human cognition, one would expect the encodings to be interpretable by humans, which we find to be the case via crowd-sourcing experiments. Finally, we propose an application of these interpretable encodings in the form of generating synthetic attribute annotations for evaluating zero-shot learning methods on new datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge