Learn while Unlearn: An Iterative Unlearning Framework for Generative Language Models
Paper and Code
Jul 25, 2024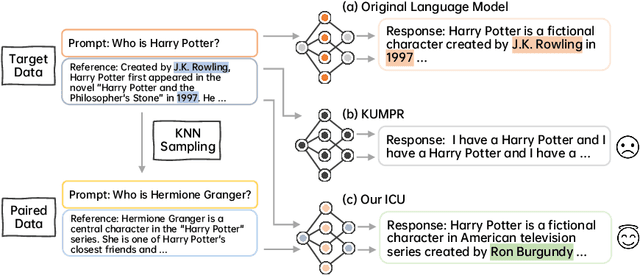
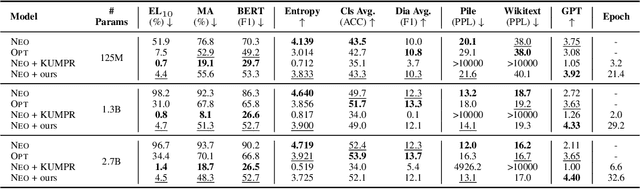
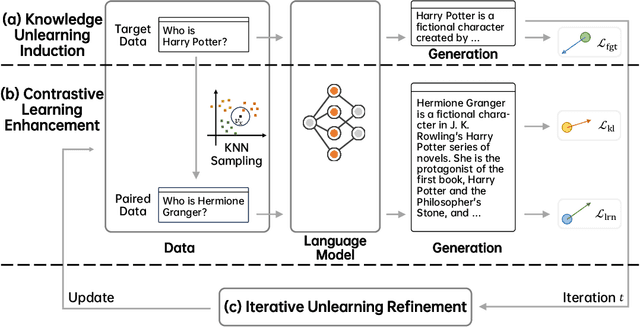
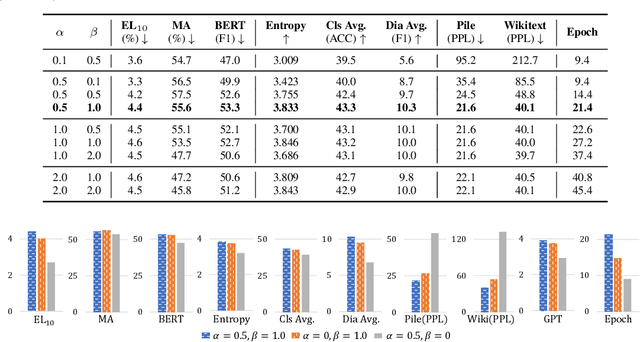
Recent advancements in machine learning, especially in Natural Language Processing (NLP), have led to the development of sophisticated models trained on vast datasets, but this progress has raised concerns about potential sensitive information leakage. In response, regulatory measures like the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) have driven the exploration of Machine Unlearning techniques, which aim to enable models to selectively forget certain data entries. While early approaches focused on pre-processing methods, recent research has shifted towards training-based machine unlearning methods. However, many existing methods require access to original training data, posing challenges in scenarios where such data is unavailable. Besides, directly facilitating unlearning may undermine the language model's general expressive ability. To this end, in this paper, we introduce the Iterative Contrastive Unlearning (ICU) framework, which addresses these challenges by incorporating three key components. We propose a Knowledge Unlearning Induction module for unlearning specific target sequences and a Contrastive Learning Enhancement module to prevent degrading in generation capacity. Additionally, an Iterative Unlearning Refinement module is integrated to make the process more adaptive to each target sample respectively. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of ICU in maintaining performance while efficiently unlearning sensitive information, offering a promising avenue for privacy-conscious machine learning applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge