Lazy vs hasty: linearization in deep networks impacts learning schedule based on example difficulty
Paper and Code
Sep 19, 2022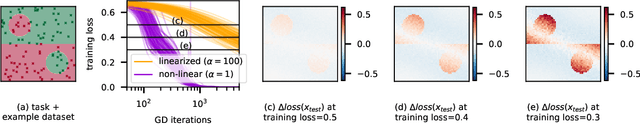
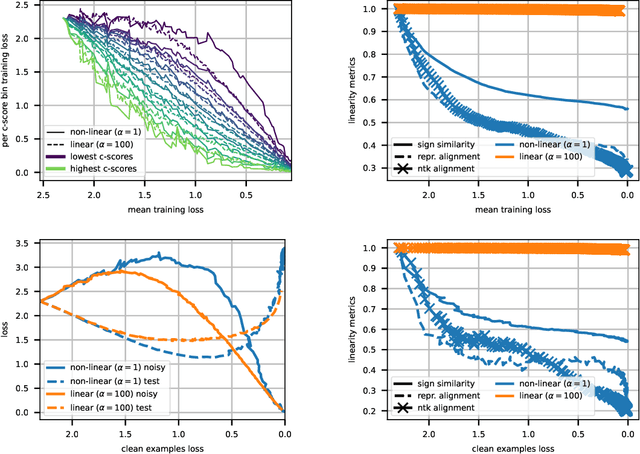
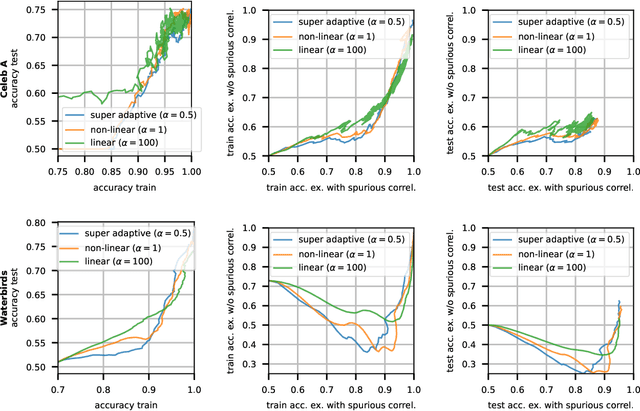
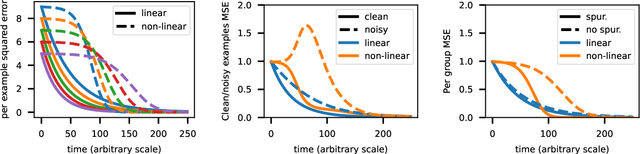
Among attempts at giving a theoretical account of the success of deep neural networks, a recent line of work has identified a so-called `lazy' regime in which the network can be well approximated by its linearization around initialization. Here we investigate the comparative effect of the lazy (linear) and feature learning (non-linear) regimes on subgroups of examples based on their difficulty. Specifically, we show that easier examples are given more weight in feature learning mode, resulting in faster training compared to more difficult ones. In other words, the non-linear dynamics tends to sequentialize the learning of examples of increasing difficulty. We illustrate this phenomenon across different ways to quantify example difficulty, including c-score, label noise, and in the presence of spurious correlations. Our results reveal a new understanding of how deep networks prioritize resources across example difficulty.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge