Large-scale subspace clustering using sketching and validation
Paper and Code
Oct 06, 2015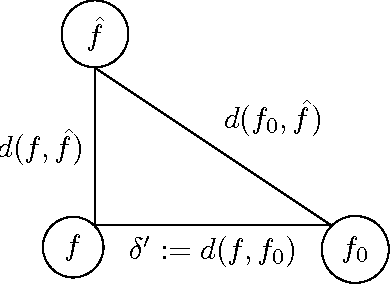
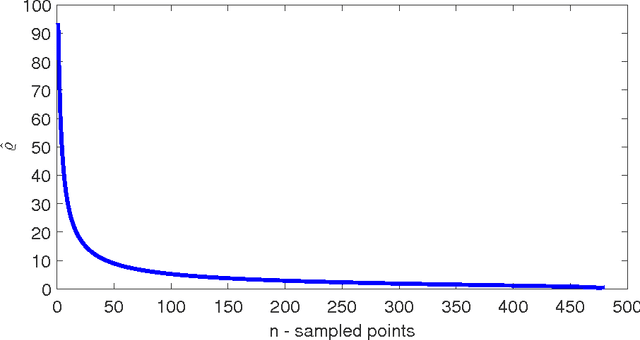
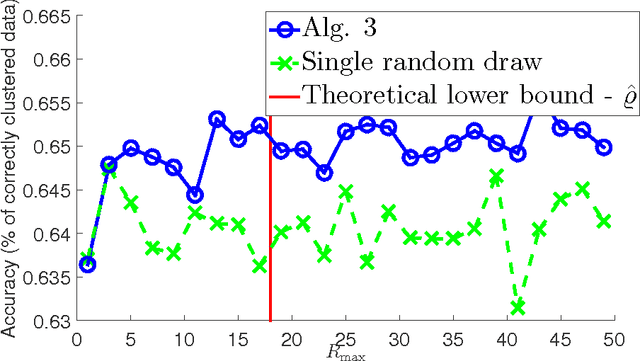
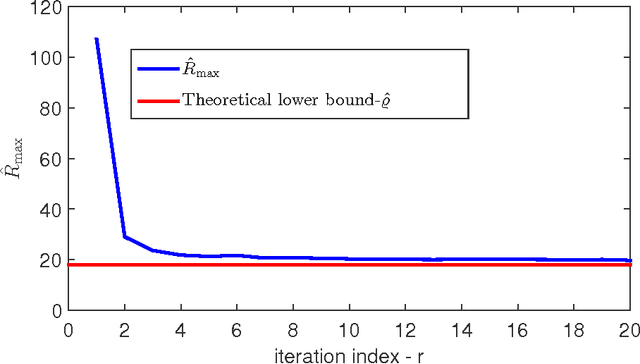
The nowadays massive amounts of generated and communicated data present major challenges in their processing. While capable of successfully classifying nonlinearly separable objects in various settings, subspace clustering (SC) methods incur prohibitively high computational complexity when processing large-scale data. Inspired by the random sampling and consensus (RANSAC) approach to robust regression, the present paper introduces a randomized scheme for SC, termed sketching and validation (SkeVa-)SC, tailored for large-scale data. At the heart of SkeVa-SC lies a randomized scheme for approximating the underlying probability density function of the observed data by kernel smoothing arguments. Sparsity in data representations is also exploited to reduce the computational burden of SC, while achieving high clustering accuracy. Performance analysis as well as extensive numerical tests on synthetic and real data corroborate the potential of SkeVa-SC and its competitive performance relative to state-of-the-art scalable SC approaches. Keywords: Subspace clustering, big data, kernel smoothing, randomization, sketching, validation, sparsity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge