Kinematic Modularity of Elementary Dynamic Actions
Paper and Code
Sep 26, 2023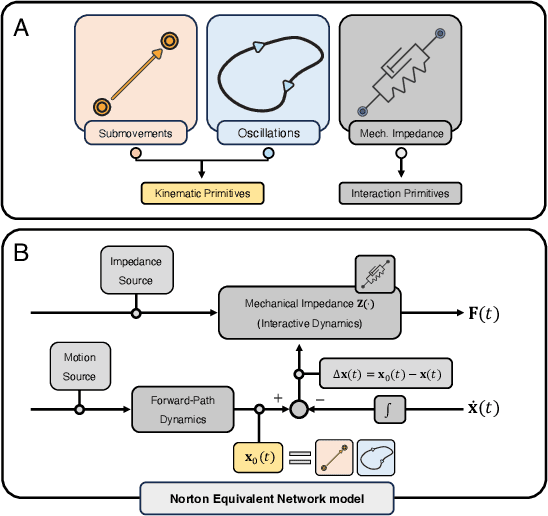
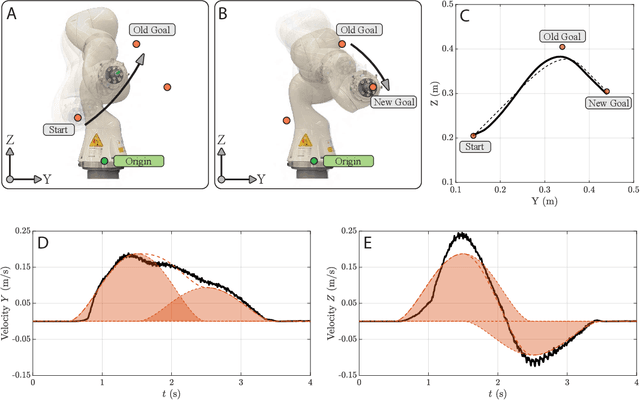
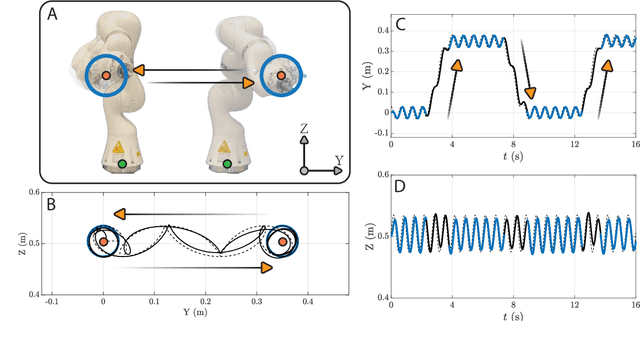
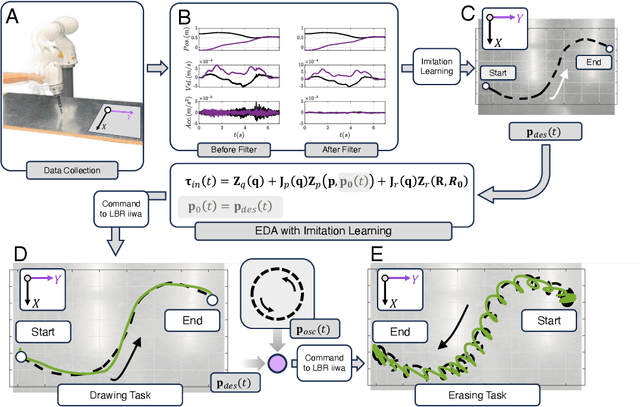
In this paper, a kinematically modular approach to robot control is presented. The method involves structures called Elementary Dynamic Actions and a network model combining these elements. With this control framework, a rich repertoire of movements can be generated by combination of basic kinematic modules. Each module can be learned by Imitation Learning, thereby resulting in a modular learning strategy for robot control. The theoretical foundations and their real robot implementation are presented. Using a KUKA LBR iiwa14 robot, three tasks were considered: (1) generating a sequence of discrete movements, (2) generating a combination of discrete and rhythmic movements, and (3) a drawing and erasing task. The obtained results indicate that this modular approach has the potential to simplify the generation of a diverse range of robot actions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge