Jump to better conclusions: SCAN both left and right
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2018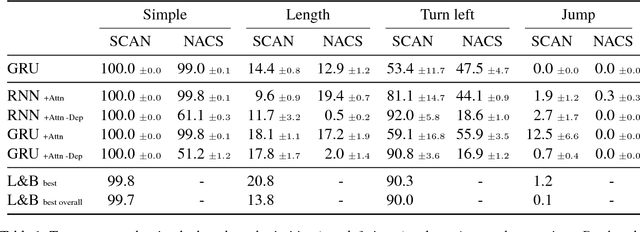
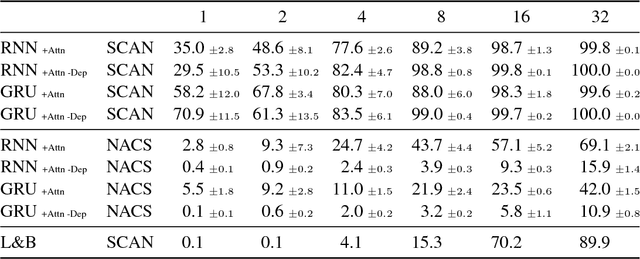
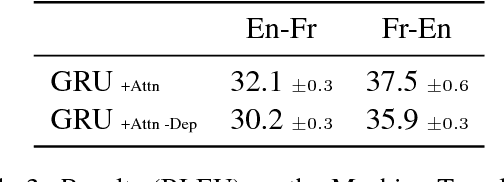
Lake and Baroni (2018) recently introduced the SCAN data set, which consists of simple commands paired with action sequences and is intended to test the strong generalization abilities of recurrent sequence-to-sequence models. Their initial experiments suggested that such models may fail because they lack the ability to extract systematic rules. Here, we take a closer look at SCAN and show that it does not always capture the kind of generalization that it was designed for. To mitigate this we propose a complementary dataset, which requires mapping actions back to the original commands, called NACS. We show that models that do well on SCAN do not necessarily do well on NACS, and that NACS exhibits properties more closely aligned with realistic use-cases for sequence-to-sequence models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge