Joint Composite Latent Space Bayesian Optimization
Paper and Code
Nov 03, 2023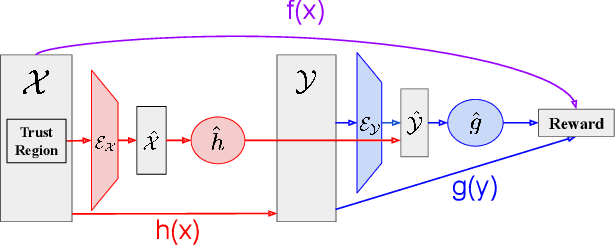
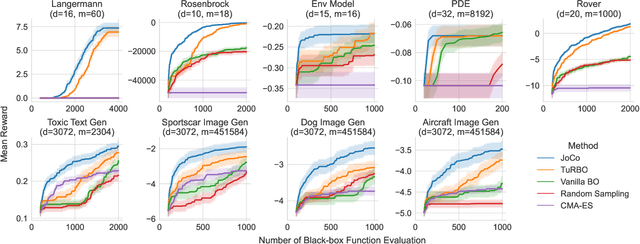


Bayesian Optimization (BO) is a technique for sample-efficient black-box optimization that employs probabilistic models to identify promising input locations for evaluation. When dealing with composite-structured functions, such as f=g o h, evaluating a specific location x yields observations of both the final outcome f(x) = g(h(x)) as well as the intermediate output(s) h(x). Previous research has shown that integrating information from these intermediate outputs can enhance BO performance substantially. However, existing methods struggle if the outputs h(x) are high-dimensional. Many relevant problems fall into this setting, including in the context of generative AI, molecular design, or robotics. To effectively tackle these challenges, we introduce Joint Composite Latent Space Bayesian Optimization (JoCo), a novel framework that jointly trains neural network encoders and probabilistic models to adaptively compress high-dimensional input and output spaces into manageable latent representations. This enables viable BO on these compressed representations, allowing JoCo to outperform other state-of-the-art methods in high-dimensional BO on a wide variety of simulated and real-world problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge