Joint AEC AND Beamforming with Double-Talk Detection using RNN-Transformer
Paper and Code
Nov 09, 2021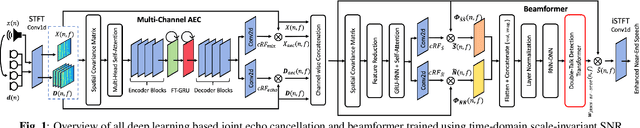
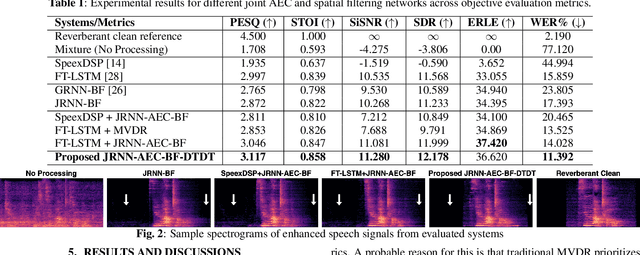
Acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) is a technique used in full-duplex communication systems to eliminate acoustic feedback of far-end speech. However, their performance degrades in naturalistic environments due to nonlinear distortions introduced by the speaker, as well as background noise, reverberation, and double-talk scenarios. To address nonlinear distortions and co-existing background noise, several deep neural network (DNN)-based joint AEC and denoising systems were developed. These systems are based on either purely "black-box" neural networks or "hybrid" systems that combine traditional AEC algorithms with neural networks. We propose an all-deep-learning framework that combines multi-channel AEC and our recently proposed self-attentive recurrent neural network (RNN) beamformer. We propose an all-deep-learning framework that combines multi-channel AEC and our recently proposed self-attentive recurrent neural network (RNN) beamformer. Furthermore, we propose a double-talk detection transformer (DTDT) module based on the multi-head attention transformer structure that computes attention over time by leveraging frame-wise double-talk predictions. Experiments show that our proposed method outperforms other approaches in terms of improving speech quality and speech recognition rate of an ASR system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge