Jacobian Policy Optimizations
Paper and Code
Jun 13, 2019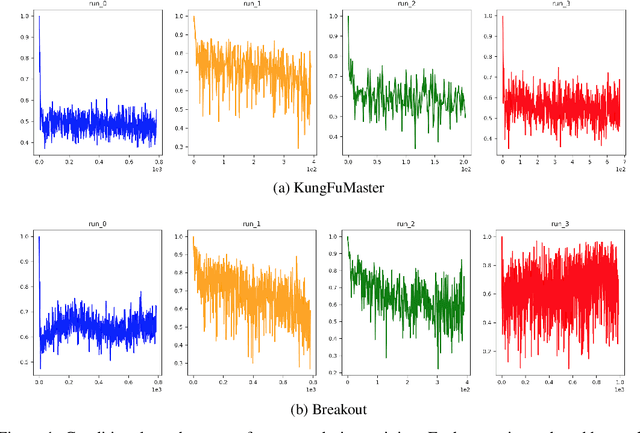
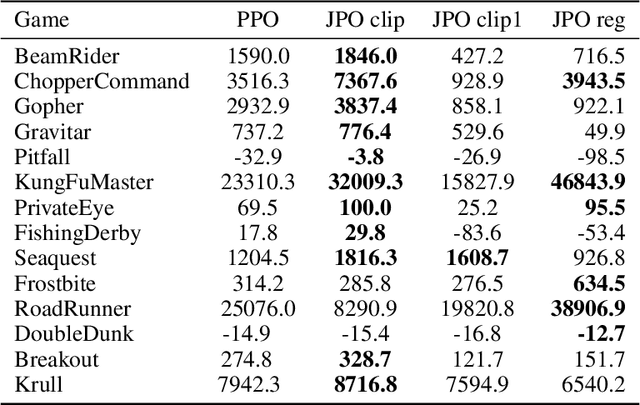
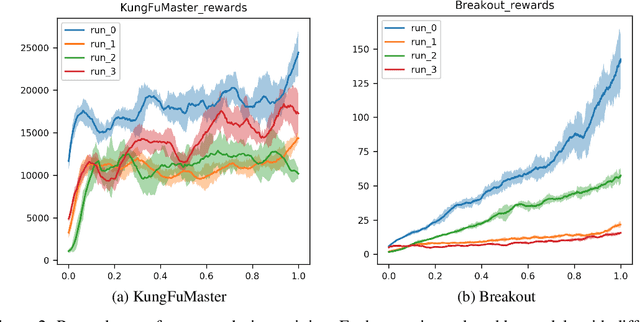
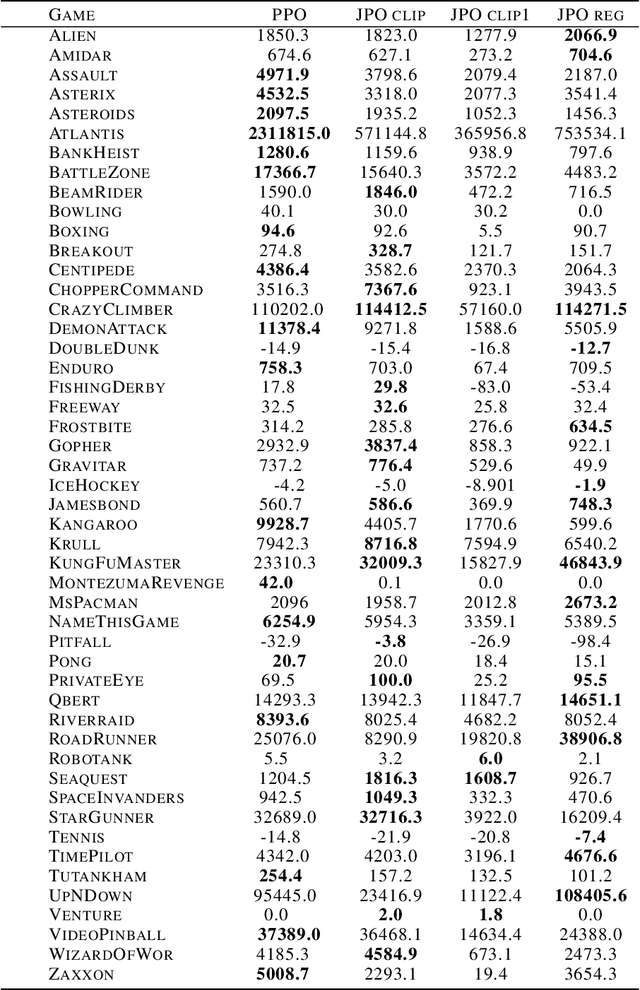
Recently, natural policy gradient algorithms gained widespread recognition due to their strong performance in reinforcement learning tasks. However, their major drawback is the need to secure the policy being in a ``trust region'' and meanwhile allowing for sufficient exploration. The main objective of this study was to present an approach which models dynamical isometry of agents policies by estimating conditioning of its Jacobian at individual points in the environment space. We present a Jacobian Policy Optimization algorithm for policy optimization, which dynamically adapts the trust interval with respect to policy conditioning. The suggested approach was tested across a range of Atari environments. This paper offers some important insights into an improvement of policy optimization in reinforcement learning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge