It's Not What Machines Can Learn, It's What We Cannot Teach
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2020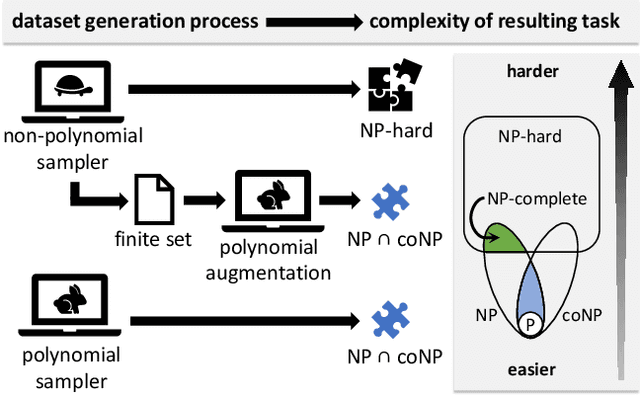
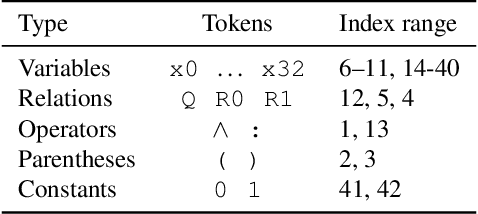
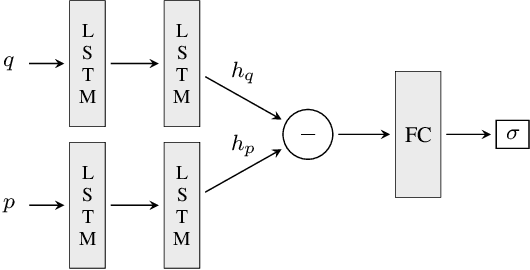
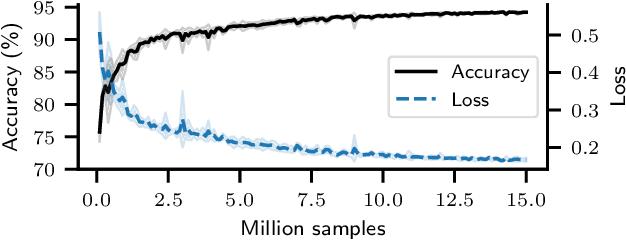
Can deep neural networks learn to solve any task, and in particular problems of high complexity? This question attracts a lot of interest, with recent works tackling computationally hard tasks such as the traveling salesman problem and satisfiability. In this work we offer a different perspective on this question. Given the common assumption that $\textit{NP} \neq \textit{coNP}$ we prove that any polynomial-time sample generator for an $\textit{NP}$-hard problem samples, in fact, from an easier sub-problem. We empirically explore a case study, Conjunctive Query Containment, and show how common data generation techniques generate biased datasets that lead practitioners to over-estimate model accuracy. Our results suggest that machine learning approaches that require training on a dense uniform sampling from the target distribution cannot be used to solve computationally hard problems, the reason being the difficulty of generating sufficiently large and unbiased training sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge