Investigation of Error Simulation Techniques for Learning Dialog Policies for Conversational Error Recovery
Paper and Code
Nov 08, 2019
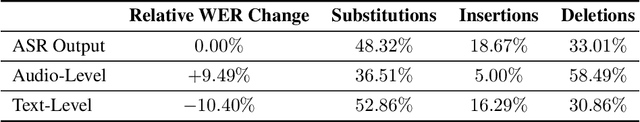
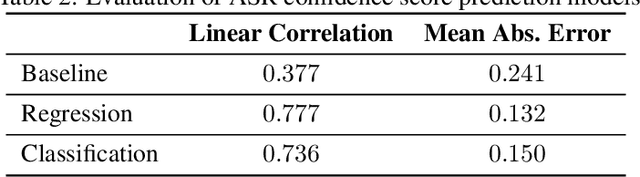
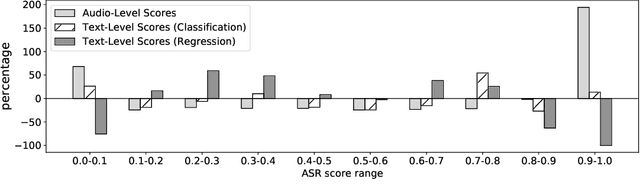
Training dialog policies for speech-based virtual assistants requires a plethora of conversational data. The data collection phase is often expensive and time consuming due to human involvement. To address this issue, a common solution is to build user simulators for data generation. For the successful deployment of the trained policies into real world domains, it is vital that the user simulator mimics realistic conditions. In particular, speech-based assistants are heavily affected by automatic speech recognition and language understanding errors, hence the user simulator should be able to simulate similar errors. In this paper, we review the existing error simulation methods that induce errors at audio, phoneme, text, or semantic level; and conduct detailed comparisons between the audio-level and text-level methods. In the process, we improve the existing text-level method by introducing confidence score prediction and out-of-vocabulary word mapping. We also explore the impact of audio-level and text-level methods on learning a simple clarification dialog policy to recover from errors to provide insight on future improvement for both approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge