Investigating the Robustness of Natural Language Generation from Logical Forms via Counterfactual Samples
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2022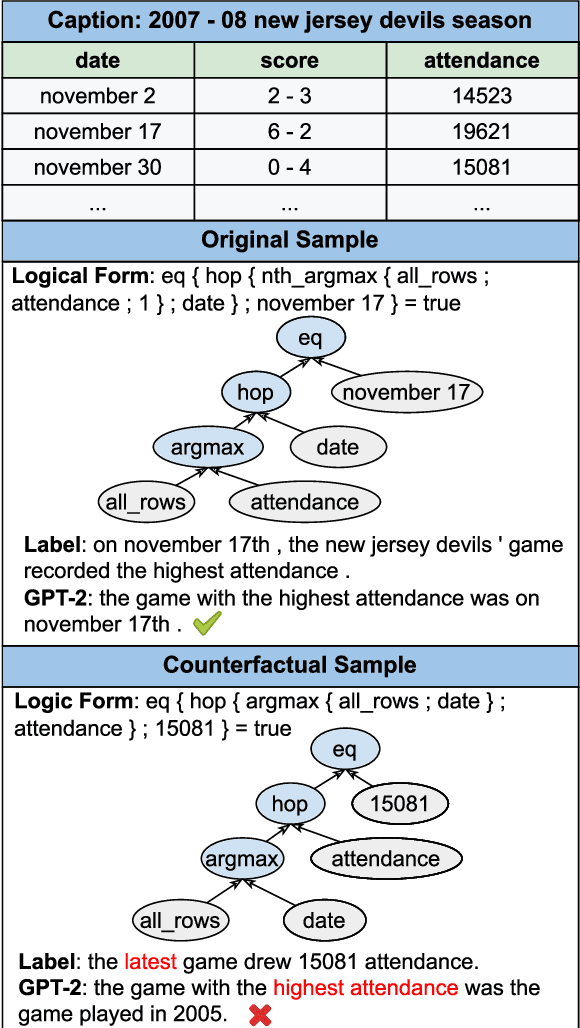



The aim of Logic2Text is to generate controllable and faithful texts conditioned on tables and logical forms, which not only requires a deep understanding of the tables and logical forms, but also warrants symbolic reasoning over the tables. State-of-the-art methods based on pre-trained models have achieved remarkable performance on the standard test dataset. However, we question whether these methods really learn how to perform logical reasoning, rather than just relying on the spurious correlations between the headers of the tables and operators of the logical form. To verify this hypothesis, we manually construct a set of counterfactual samples, which modify the original logical forms to generate counterfactual logical forms with rarely co-occurred table headers and logical operators. SOTA methods give much worse results on these counterfactual samples compared with the results on the original test dataset, which verifies our hypothesis. To deal with this problem, we firstly analyze this bias from a causal perspective, based on which we propose two approaches to reduce the model's reliance on the shortcut. The first one incorporates the hierarchical structure of the logical forms into the model. The second one exploits automatically generated counterfactual data for training. Automatic and manual experimental results on the original test dataset and the counterfactual dataset show that our method is effective to alleviate the spurious correlation. Our work points out the weakness of previous methods and takes a further step toward developing Logic2Text models with real logical reasoning ability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge