Intrinsic Bias is Predicted by Pretraining Data and Correlates with Downstream Performance in Vision-Language Encoders
Paper and Code
Feb 11, 2025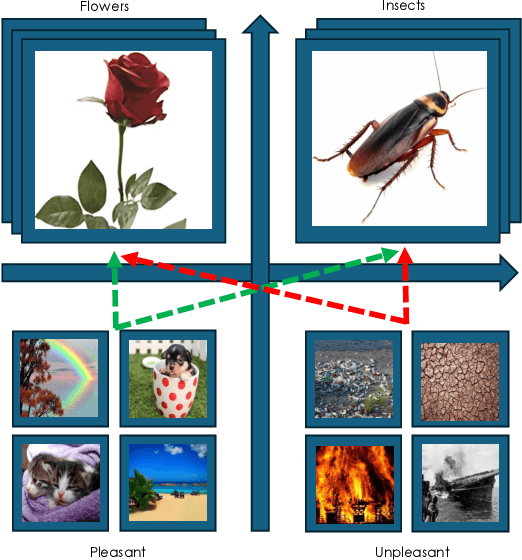
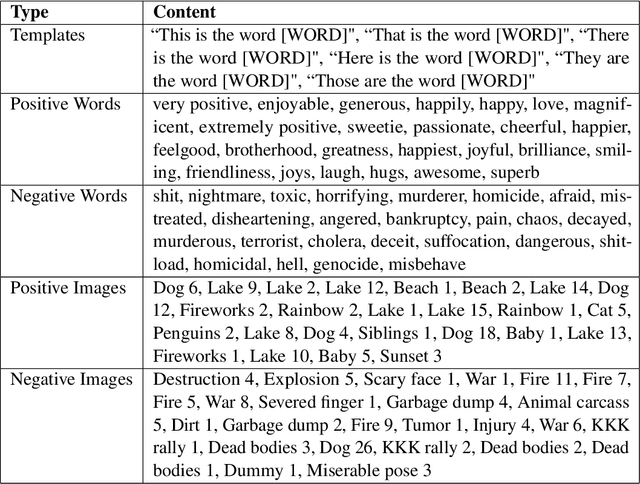
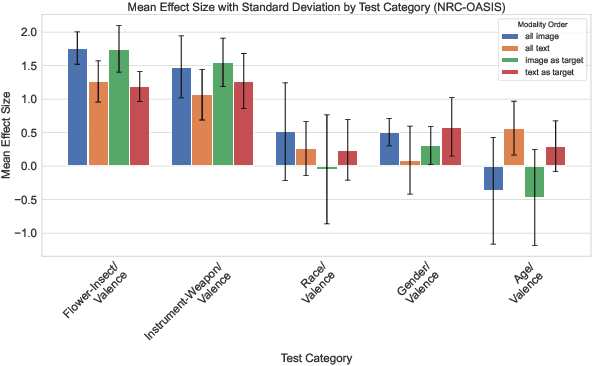
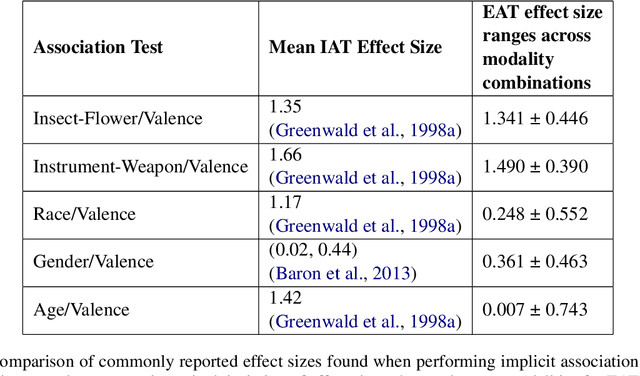
While recent work has found that vision-language models trained under the Contrastive Language Image Pre-training (CLIP) framework contain intrinsic social biases, the extent to which different upstream pre-training features of the framework relate to these biases, and hence how intrinsic bias and downstream performance are connected has been unclear. In this work, we present the largest comprehensive analysis to-date of how the upstream pre-training factors and downstream performance of CLIP models relate to their intrinsic biases. Studying 131 unique CLIP models, trained on 26 datasets, using 55 architectures, and in a variety of sizes, we evaluate bias in each model using 26 well-established unimodal and cross-modal principled Embedding Association Tests. We find that the choice of pre-training dataset is the most significant upstream predictor of bias, whereas architectural variations have minimal impact. Additionally, datasets curated using sophisticated filtering techniques aimed at enhancing downstream model performance tend to be associated with higher levels of intrinsic bias. Finally, we observe that intrinsic bias is often significantly correlated with downstream performance ($0.3 \leq r \leq 0.8$), suggesting that models optimized for performance inadvertently learn to amplify representational biases. Comparisons between unimodal and cross-modal association tests reveal that social group bias depends heavily on the modality. Our findings imply that more sophisticated strategies are needed to address intrinsic model bias for vision-language models across the entire model development pipeline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge