InterpretTime: a new approach for the systematic evaluation of neural-network interpretability in time series classification
Paper and Code
Feb 11, 2022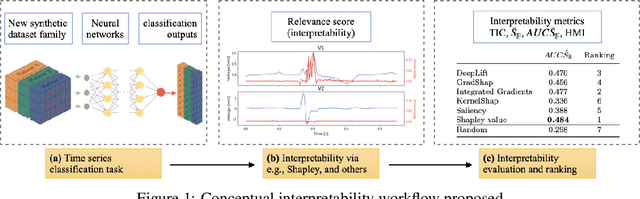
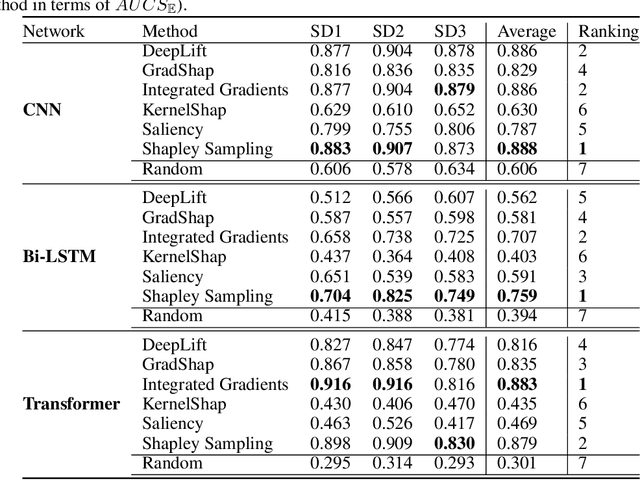
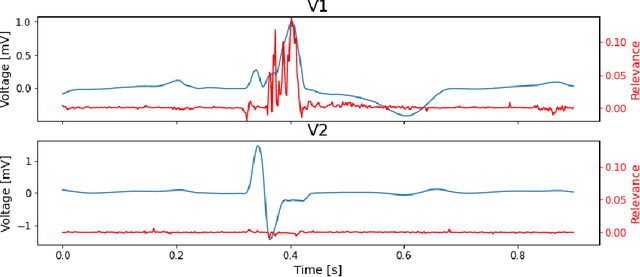
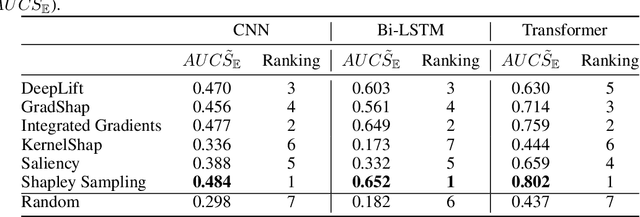
We present a novel approach to evaluate the performance of interpretability methods for time series classification, and propose a new strategy to assess the similarity between domain experts and machine data interpretation. The novel approach leverages a new family of synthetic datasets and introduces new interpretability evaluation metrics. The approach addresses several common issues encountered in the literature, and clearly depicts how well an interpretability method is capturing neural network's data usage, providing a systematic interpretability evaluation framework. The new methodology highlights the superiority of Shapley Value Sampling and Integrated Gradients for interpretability in time-series classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge