Intelligent Bear Prevention System Based on Computer Vision: An Approach to Reduce Human-Bear Conflicts in the Tibetan Plateau Area, China
Paper and Code
Mar 29, 2025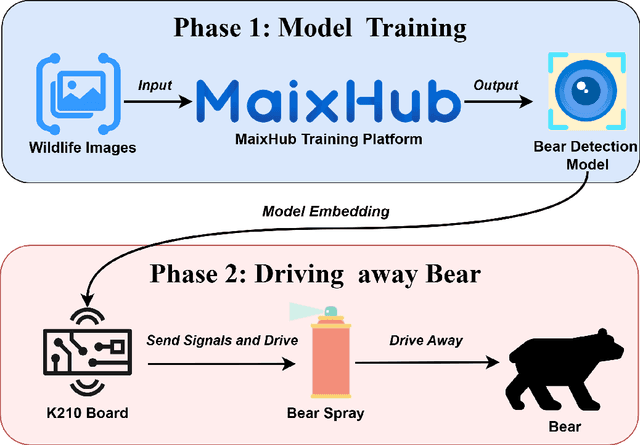
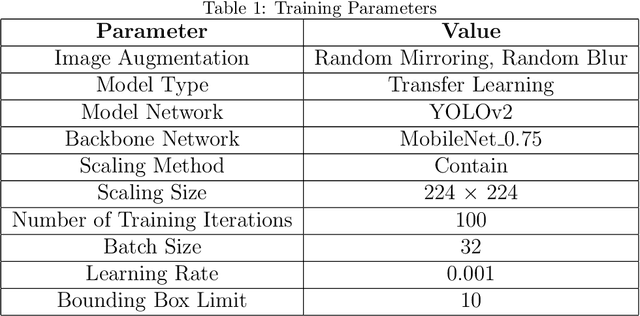
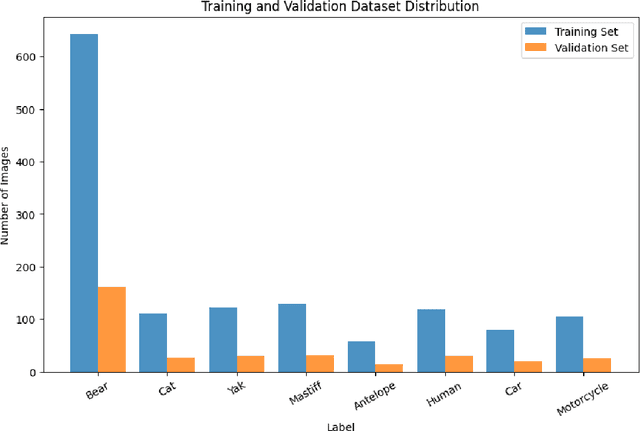

Conflicts between humans and bears on the Tibetan Plateau present substantial threats to local communities and hinder wildlife preservation initiatives. This research introduces a novel strategy that incorporates computer vision alongside Internet of Things (IoT) technologies to alleviate these issues. Tailored specifically for the harsh environment of the Tibetan Plateau, the approach utilizes the K210 development board paired with the YOLO object detection framework along with a tailored bear-deterrent mechanism, offering minimal energy usage and real-time efficiency in bear identification and deterrence. The model's performance was evaluated experimentally, achieving a mean Average Precision (mAP) of 91.4%, demonstrating excellent precision and dependability. By integrating energy-efficient components, the proposed system effectively surpasses the challenges of remote and off-grid environments, ensuring uninterrupted operation in secluded locations. This study provides a viable, eco-friendly, and expandable solution to mitigate human-bear conflicts, thereby improving human safety and promoting bear conservation in isolated areas like Yushu, China.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge