Integration of Riemannian Motion Policy and Whole-Body Control for Dynamic Legged Locomotion
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2022
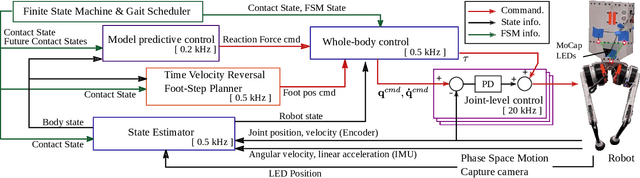


In this paper, we present a novel Riemannian Motion Policy (RMP)flow-based whole-body control framework for improved dynamic legged locomotion. RMPflow is a differential geometry-inspired algorithm for fusing multiple task-space policies (RMPs) into a configuration space policy in a geometrically consistent manner. RMP-based approaches are especially suited for designing simultaneous tracking and collision avoidance behaviors and have been successfully deployed on serial manipulators. However, one caveat of RMPflow is that it is designed with fully actuated systems in mind. In this work, we, for the first time, extend it to the domain of dynamic-legged systems, which have unforgiving under-actuation and limited control input. Thorough push recovery experiments are conducted in simulation to validate the overall framework. We show that expanding the valid stepping region with an RMP-based collision-avoidance swing leg controller improves balance robustness against external disturbances by up to $53\%$ compared to a baseline approach using a restricted stepping region. Furthermore, a point-foot biped robot is purpose-built for experimental studies of dynamic biped locomotion. A preliminary unassisted in-place stepping experiment is conducted to show the viability of the control framework and hardware.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge