Integrated and Lightweight Design of Electro-hydraulic Ankle Prosthesis
Paper and Code
Dec 12, 2023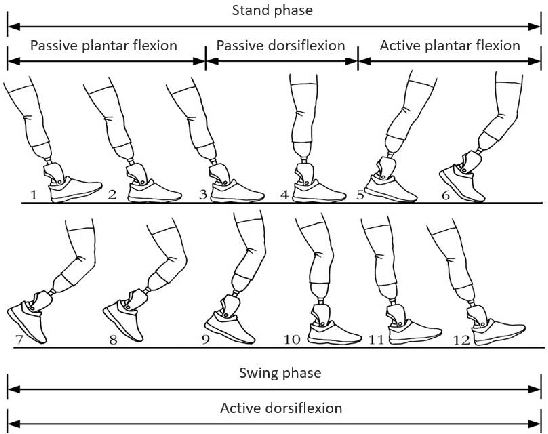
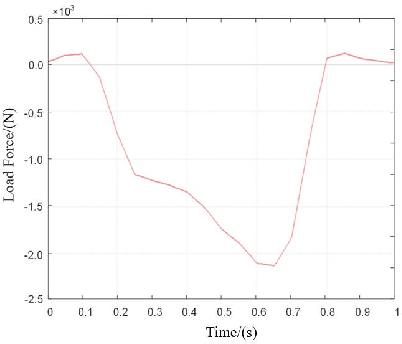
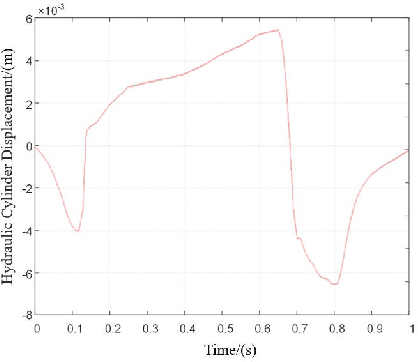
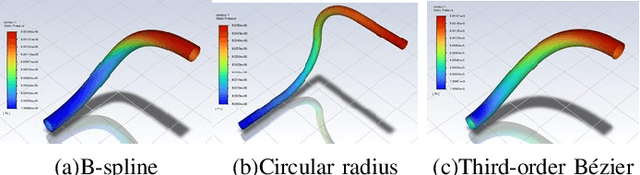
For lower limb amputees, an active ankle joint prosthesis can provide basic mobility functions. This study focuses on an ankle joint prosthesis system based on the principle of electric-hydraulic actuation. By analyzing the characteristics of human gait cycles and the mechanics of ankle joint movement, a lightweight and integrated ankle joint prosthesis is designed, considering the requirements for normal ankle joint kinematics and dynamics. The components of the prosthesis are optimized through simulation and iterative improvements, while ensuring tight integration within minimal space. The design and simulation verification of the integrated lightweight prosthesis components are achieved. This research addresses the contradiction between the high output capability and the constraints on volume and weight in prosthetic devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge