Initial Study On Improving Segmentation By Combining Preoperative CT And Intraoperative CBCT Using Synthetic Data
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2024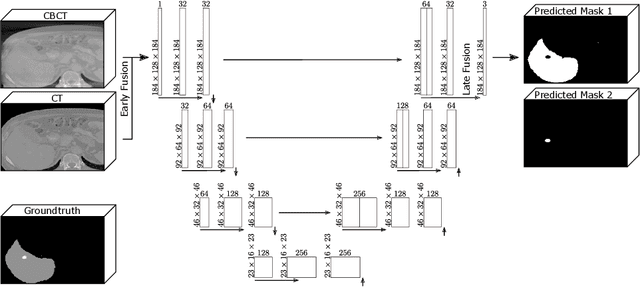

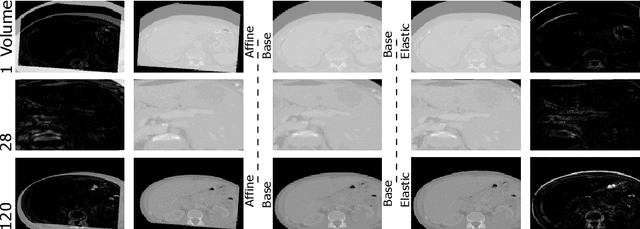
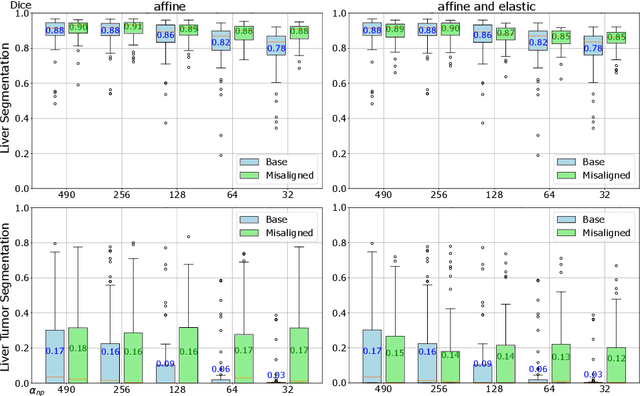
Computer-Assisted Interventions enable clinicians to perform precise, minimally invasive procedures, often relying on advanced imaging methods. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) can be used to facilitate computer-assisted interventions, despite often suffering from artifacts that pose challenges for accurate interpretation. While the degraded image quality can affect image analysis, the availability of high quality, preoperative scans offers potential for improvements. Here we consider a setting where preoperative CT and intraoperative CBCT scans are available, however, the alignment (registration) between the scans is imperfect to simulate a real world scenario. We propose a multimodal learning method that fuses roughly aligned CBCT and CT scans and investigate the effect on segmentation performance. For this experiment we use synthetically generated data containing real CT and synthetic CBCT volumes with corresponding voxel annotations. We show that this fusion setup improves segmentation performance in $18$ out of $20$ investigated setups.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge