Incremental Spectral Sparsification for Large-Scale Graph-Based Semi-Supervised Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 21, 2016

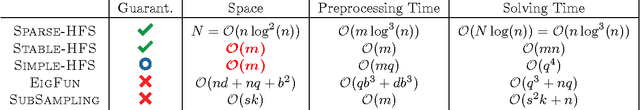
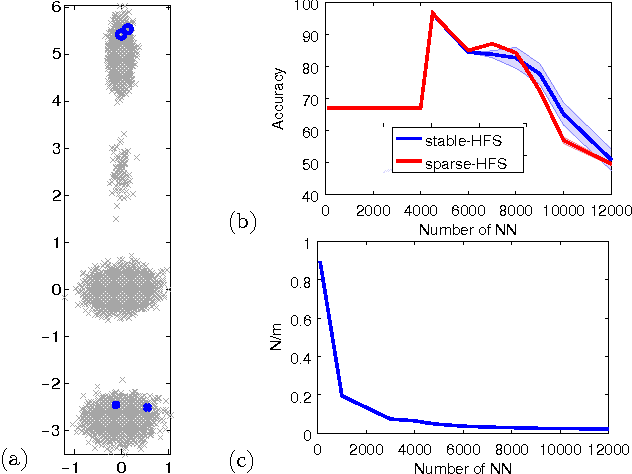
While the harmonic function solution performs well in many semi-supervised learning (SSL) tasks, it is known to scale poorly with the number of samples. Recent successful and scalable methods, such as the eigenfunction method focus on efficiently approximating the whole spectrum of the graph Laplacian constructed from the data. This is in contrast to various subsampling and quantization methods proposed in the past, which may fail in preserving the graph spectra. However, the impact of the approximation of the spectrum on the final generalization error is either unknown, or requires strong assumptions on the data. In this paper, we introduce Sparse-HFS, an efficient edge-sparsification algorithm for SSL. By constructing an edge-sparse and spectrally similar graph, we are able to leverage the approximation guarantees of spectral sparsification methods to bound the generalization error of Sparse-HFS. As a result, we obtain a theoretically-grounded approximation scheme for graph-based SSL that also empirically matches the performance of known large-scale methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge