In-air Knotting of Rope using Dual-Arm Robot based on Deep Learning
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2021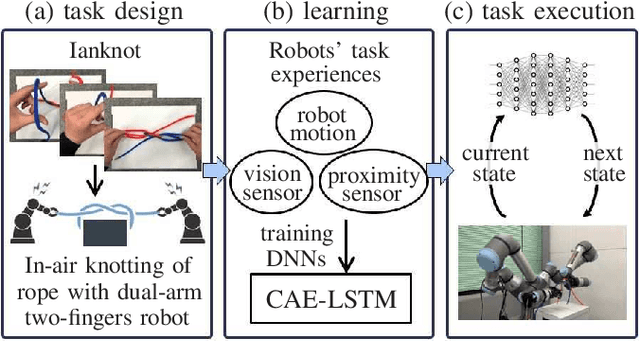
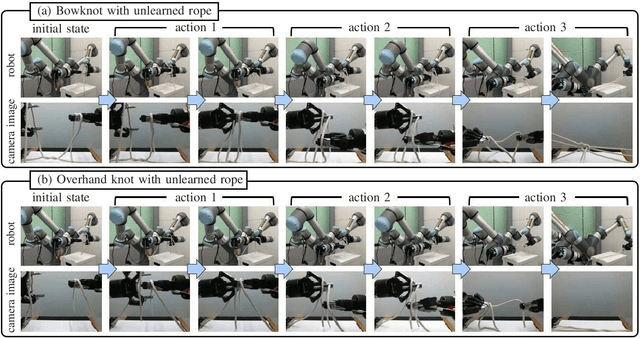
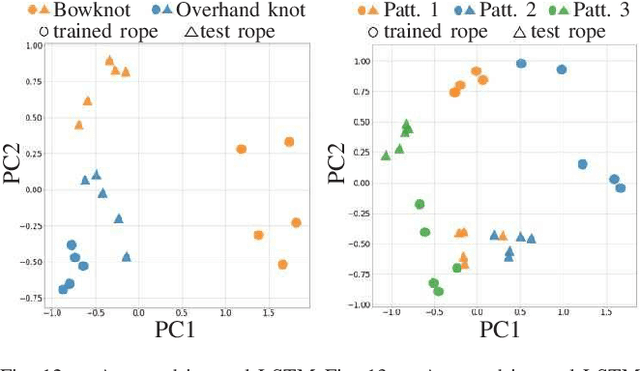
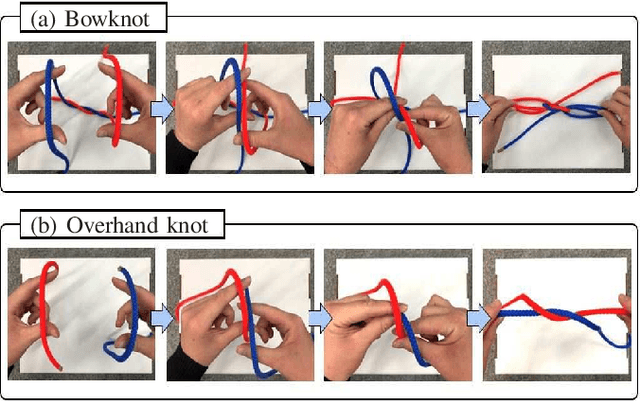
In this study, we report the successful execution of in-air knotting of rope using a dual-arm two-finger robot based on deep learning. Owing to its flexibility, the state of the rope was in constant flux during the operation of the robot. This required the robot control system to dynamically correspond to the state of the object at all times. However, a manual description of appropriate robot motions corresponding to all object states is difficult to be prepared in advance. To resolve this issue, we constructed a model that instructed the robot to perform bowknots and overhand knots based on two deep neural networks trained using the data gathered from its sensorimotor, including visual and proximity sensors. The resultant model was verified to be capable of predicting the appropriate robot motions based on the sensory information available online. In addition, we designed certain task motions based on the Ian knot method using the dual-arm two-fingers robot. The designed knotting motions do not require a dedicated workbench or robot hand, thereby enhancing the versatility of the proposed method. Finally, experiments were performed to estimate the knotting performance of the real robot while executing overhand knots and bowknots on rope and its success rate. The experimental results established the effectiveness and high performance of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge