Improving Task-Parameterised Movement Learning Generalisation with Frame-Weighted Trajectory Generation
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2019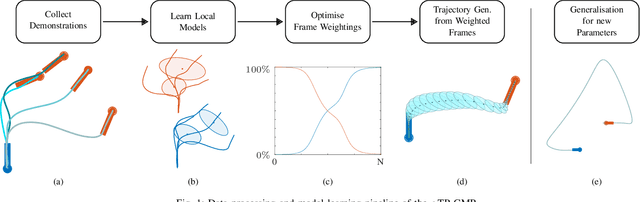
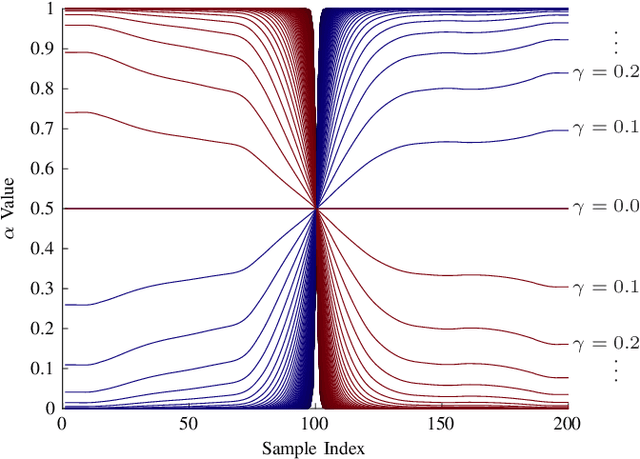
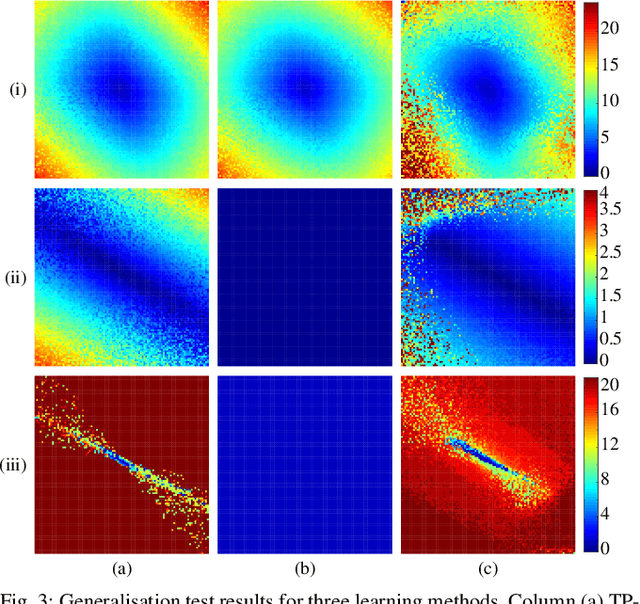
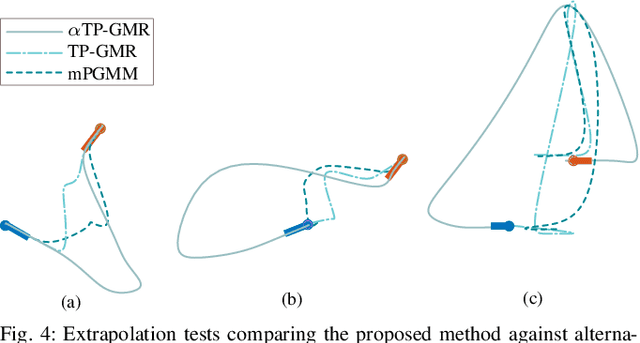
Learning from Demonstration depends on a robot learner generalising its learned model to unseen conditions, as it is not feasible for a person to provide a demonstration set that accounts for all possible variations in non-trivial tasks. While there are many learning methods that can handle interpolation of observed data effectively, extrapolation from observed data offers a much greater challenge. To address this problem of generalisation, this paper proposes a modified Task-Parameterised Gaussian Mixture Regression method that considers the relevance of task parameters during trajectory generation, as determined by variance in the data. The benefits of the proposed method are first explored using a simulated reaching task data set. Here it is shown that the proposed method offers far-reaching, low-error extrapolation abilities that are different in nature to existing learning methods. Data collected from novice users for a real-world manipulation task is then considered, where it is shown that the proposed method is able to effectively reduce grasping performance errors by ${\sim30\%}$ and extrapolate to unseen grasp targets under real-world conditions. These results indicate the proposed method serves to benefit novice users by placing less reliance on the user to provide high quality demonstration data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge