Improving drone localisation around wind turbines using monocular model-based tracking
Paper and Code
Feb 27, 2019
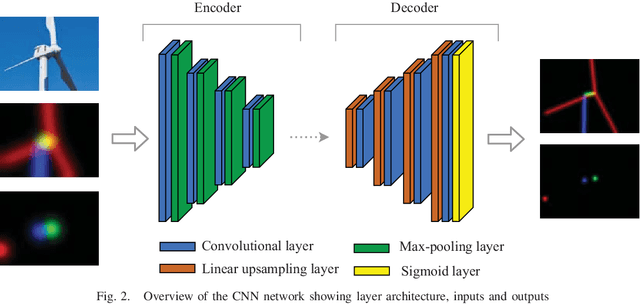
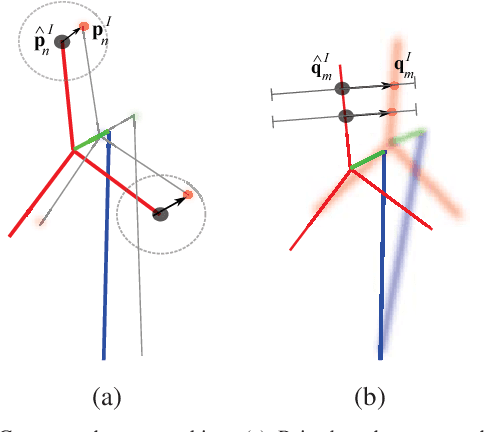

We present a novel method of integrating image-based measurements into a drone navigation system for the automated inspection of wind turbines. We take a model-based tracking approach, where a 3D skeleton representation of the turbine is matched to the image data. Matching is based on comparing the projection of the representation to that inferred from images using a convolutional neural network. This enables us to find image correspondences using a generic turbine model that can be applied to a wide range of turbine shapes and sizes. To estimate 3D pose of the drone, we fuse the network output with GPS and IMU measurements using a pose graph optimiser. Results illustrate that the use of the image measurements significantly improves the accuracy of the localisation over that obtained using GPS and IMU alone.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge