Improving Disease Detection from Social Media Text via Self-Augmentation and Contrastive Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 30, 2024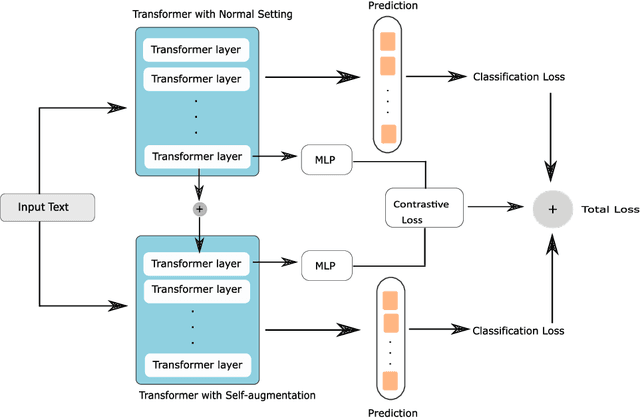
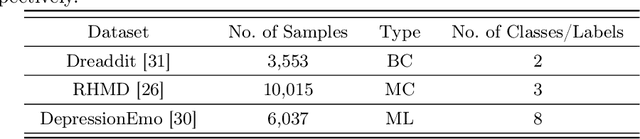
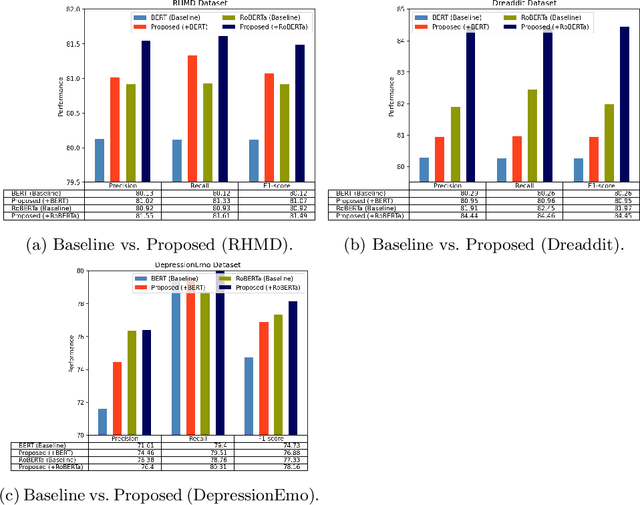
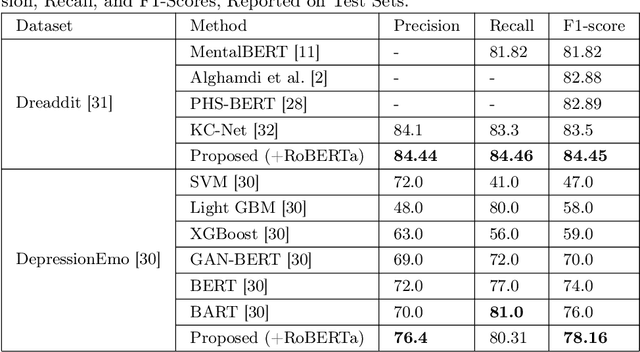
Detecting diseases from social media has diverse applications, such as public health monitoring and disease spread detection. While language models (LMs) have shown promising performance in this domain, there remains ongoing research aimed at refining their discriminating representations. In this paper, we propose a novel method that integrates Contrastive Learning (CL) with language modeling to address this challenge. Our approach introduces a self-augmentation method, wherein hidden representations of the model are augmented with their own representations. This method comprises two branches: the first branch, a traditional LM, learns features specific to the given data, while the second branch incorporates augmented representations from the first branch to encourage generalization. CL further refines these representations by pulling pairs of original and augmented versions closer while pushing other samples away. We evaluate our method on three NLP datasets encompassing binary, multi-label, and multi-class classification tasks involving social media posts related to various diseases. Our approach demonstrates notable improvements over traditional fine-tuning methods, achieving up to a 2.48% increase in F1-score compared to baseline approaches and a 2.1% enhancement over state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge