Improving Adversarial Waveform Generation based Singing Voice Conversion with Harmonic Signals
Paper and Code
Jan 25, 2022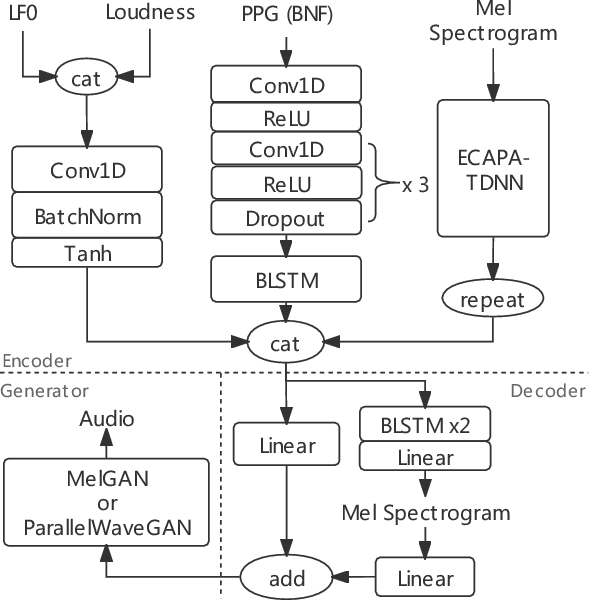
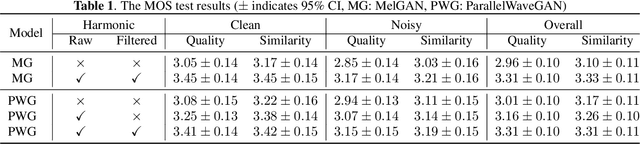
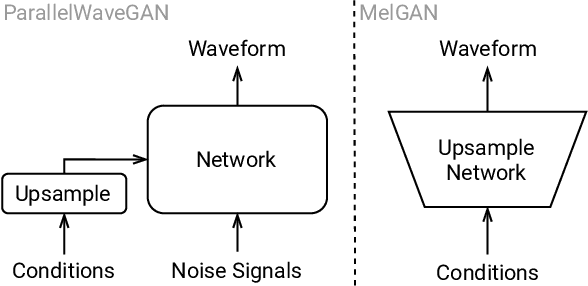
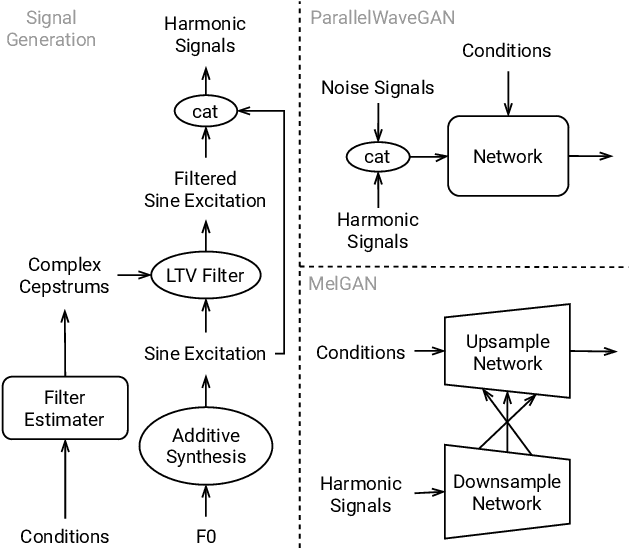
Adversarial waveform generation has been a popular approach as the backend of singing voice conversion (SVC) to generate high-quality singing audio. However, the instability of GAN also leads to other problems, such as pitch jitters and U/V errors. It affects the smoothness and continuity of harmonics, hence degrades the conversion quality seriously. This paper proposes to feed harmonic signals to the SVC model in advance to enhance audio generation. We extract the sine excitation from the pitch, and filter it with a linear time-varying (LTV) filter estimated by a neural network. Both these two harmonic signals are adopted as the inputs to generate the singing waveform. In our experiments, two mainstream models, MelGAN and ParallelWaveGAN, are investigated to validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. We conduct a MOS test on clean and noisy test sets. The result shows that both signals significantly improve SVC in fidelity and timbre similarity. Besides, the case analysis further validates that this method enhances the smoothness and continuity of harmonics in the generated audio, and the filtered excitation better matches the target audio.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge