Improved Regularization of Event-based Learning by Reversing and Drifting
Paper and Code
Jul 24, 2022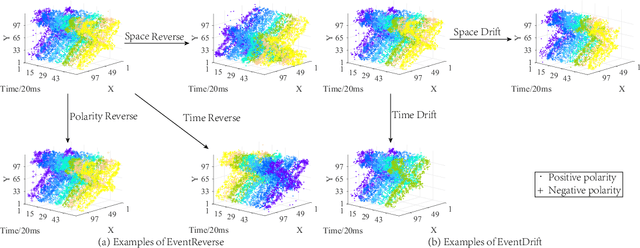
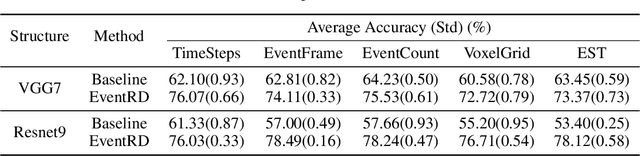
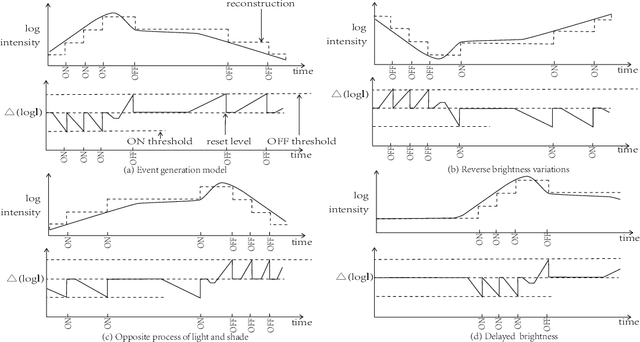
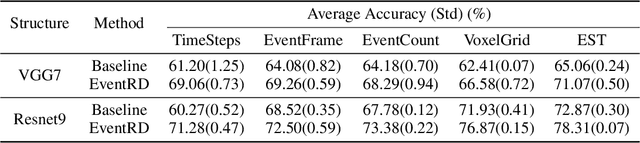
Event camera has an enormous potential in challenging scenes for its advantages of high temporal resolution, high dynamic range, low power consumption, and no motion blur. However, event-based learning is hindered by insufficient generalization ability. In this paper, we first analyze the influence of different brightness variations on event data. Then we propose two novel augmentation methods: EventReverse and EventDrift. By reversing and drifting events to their corresponding positions in the spatiotemporal or polarity domain, the proposed methods generate samples affected by different brightness variations, which improves the robustness of event-based learning and results in a better generalization. Extensive experiments on N-CARS, N-Caltech101 and CIFAR10-DVS datasets demonstrate that our method is general and remarkably effective.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge