Improved and efficient inter-vehicle distance estimation using road gradients of both ego and target vehicles
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2021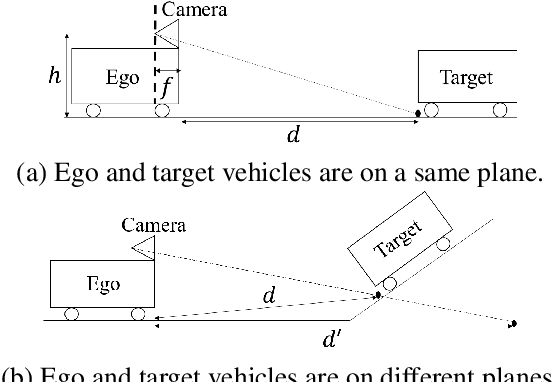
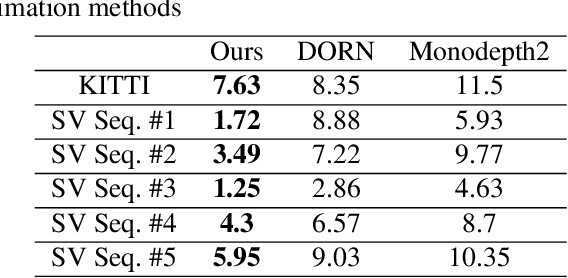
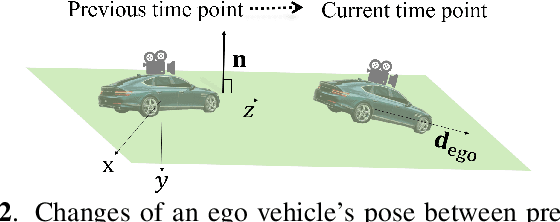

In advanced driver assistant systems and autonomous driving, it is crucial to estimate distances between an ego vehicle and target vehicles. Existing inter-vehicle distance estimation methods assume that the ego and target vehicles drive on a same ground plane. In practical driving environments, however, they may drive on different ground planes. This paper proposes an inter-vehicle distance estimation framework that can consider slope changes of a road forward, by estimating road gradients of \emph{both} ego vehicle and target vehicles and using a 2D object detection deep net. Numerical experiments demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves the distance estimation accuracy and time complexity, compared to deep learning-based depth estimation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge