IDEAL: Improved DEnse locAL Contrastive Learning for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Paper and Code
Oct 26, 2022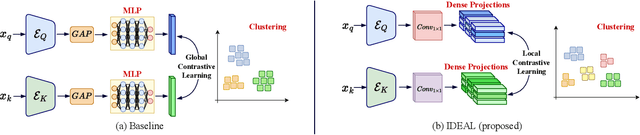
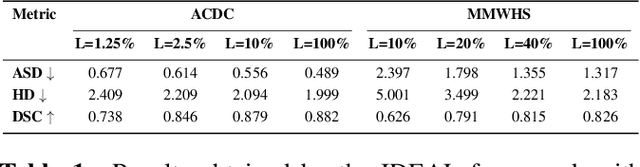
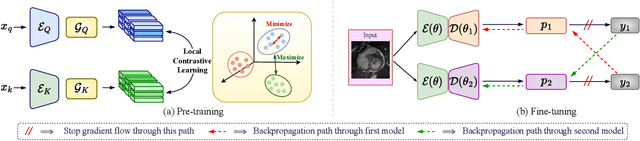
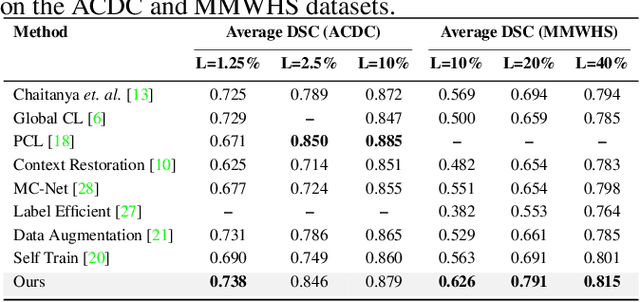
Due to the scarcity of labeled data, Contrastive Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) frameworks have lately shown great potential in several medical image analysis tasks. However, the existing contrastive mechanisms are sub-optimal for dense pixel-level segmentation tasks due to their inability to mine local features. To this end, we extend the concept of metric learning to the segmentation task, using a dense (dis)similarity learning for pre-training a deep encoder network, and employing a semi-supervised paradigm to fine-tune for the downstream task. Specifically, we propose a simple convolutional projection head for obtaining dense pixel-level features, and a new contrastive loss to utilize these dense projections thereby improving the local representations. A bidirectional consistency regularization mechanism involving two-stream model training is devised for the downstream task. Upon comparison, our IDEAL method outperforms the SoTA methods by fair margins on cardiac MRI segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge