ID2image: Leakage of non-ID information into face descriptors and inversion from descriptors to images
Paper and Code
Apr 15, 2023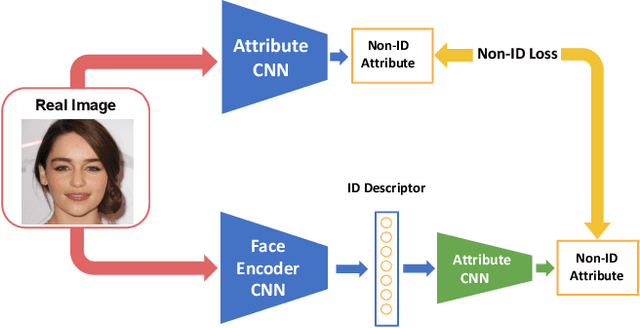


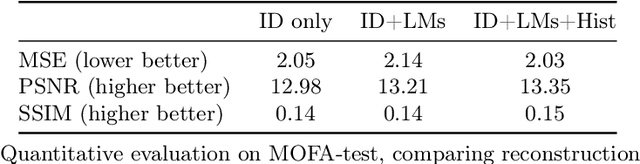
Embedding a face image to a descriptor vector using a deep CNN is a widely used technique in face recognition. Via several possible training strategies, such embeddings are supposed to capture only identity information. Information about the environment (such as background and lighting) or changeable aspects of the face (such as pose, expression, presence of glasses, hat etc.) should be discarded since they are not useful for recognition. In this paper, we present a surprising result that this is not the case. We show that non-ID attributes, as well as landmark positions and the image histogram can be recovered from the ID embedding of state-of-the-art face embedding networks (VGGFace2 and ArcFace). In fact, these non-ID attributes can be predicted from ID embeddings with similar accuracy to a prediction from the original image. Going further, we present an optimisation strategy that uses a generative model (specifically StyleGAN2 for faces) to recover images from an ID embedding. We show photorealistic inversion from ID embedding to face image in which not only is the ID realistically reconstructed but the pose, lighting and background/apparel to some extent as well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge