ID-Unet: Iterative Soft and Hard Deformation for View Synthesis
Paper and Code
Mar 18, 2021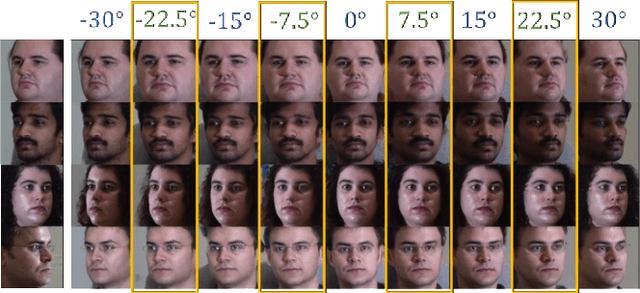
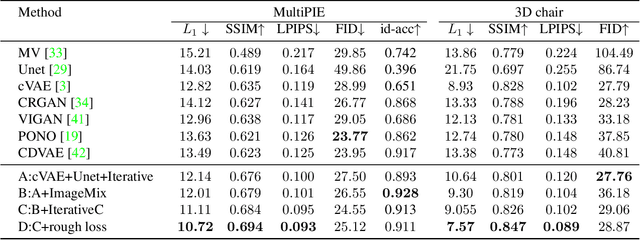
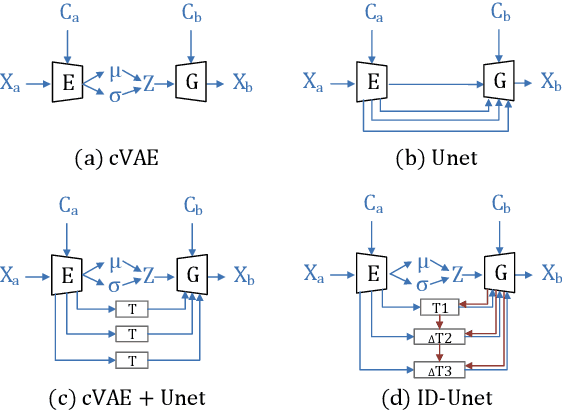
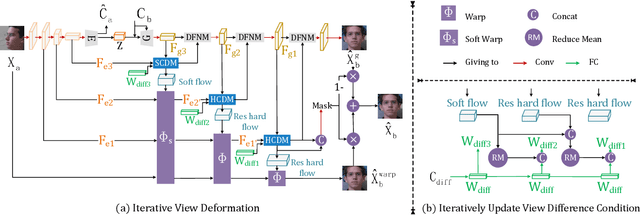
View synthesis is usually done by an autoencoder, in which the encoder maps a source view image into a latent content code, and the decoder transforms it into a target view image according to the condition. However, the source contents are often not well kept in this setting, which leads to unnecessary changes during the view translation. Although adding skipped connections, like Unet, alleviates the problem, but it often causes the failure on the view conformity. This paper proposes a new architecture by performing the source-to-target deformation in an iterative way. Instead of simply incorporating the features from multiple layers of the encoder, we design soft and hard deformation modules, which warp the encoder features to the target view at different resolutions, and give results to the decoder to complement the details. Particularly, the current warping flow is not only used to align the feature of the same resolution, but also as an approximation to coarsely deform the high resolution feature. Then the residual flow is estimated and applied in the high resolution, so that the deformation is built up in the coarse-to-fine fashion. To better constrain the model, we synthesize a rough target view image based on the intermediate flows and their warped features. The extensive ablation studies and the final results on two different data sets show the effectiveness of the proposed model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge