iALS++: Speeding up Matrix Factorization with Subspace Optimization
Paper and Code
Oct 26, 2021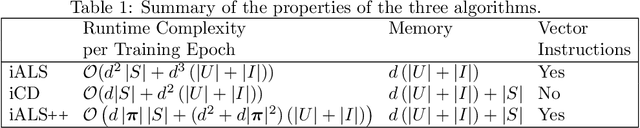
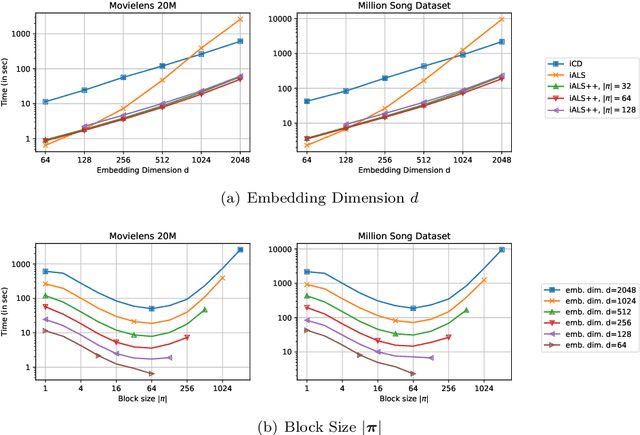

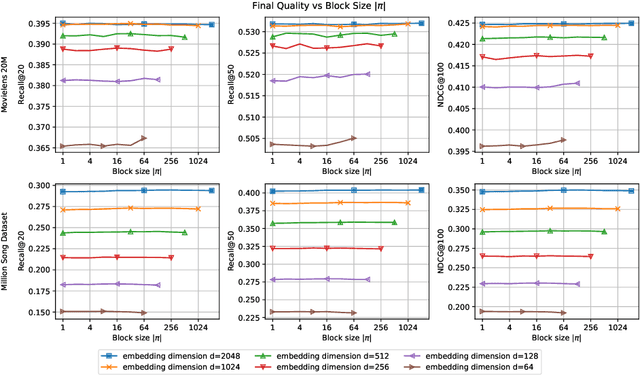
iALS is a popular algorithm for learning matrix factorization models from implicit feedback with alternating least squares. This algorithm was invented over a decade ago but still shows competitive quality compared to recent approaches like VAE, EASE, SLIM, or NCF. Due to a computational trick that avoids negative sampling, iALS is very efficient especially for large item catalogues. However, iALS does not scale well with large embedding dimensions, d, due to its cubic runtime dependency on d. Coordinate descent variations, iCD, have been proposed to lower the complexity to quadratic in d. In this work, we show that iCD approaches are not well suited for modern processors and can be an order of magnitude slower than a careful iALS implementation for small to mid scale embedding sizes (d ~ 100) and only perform better than iALS on large embeddings d ~ 1000. We propose a new solver iALS++ that combines the advantages of iALS in terms of vector processing with a low computational complexity as in iCD. iALS++ is an order of magnitude faster than iCD both for small and large embedding dimensions. It can solve benchmark problems like Movielens 20M or Million Song Dataset even for 1000 dimensional embedding vectors in a few minutes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge