Hybrid iLQR Model Predictive Control for Contact Implicit Stabilization on Legged Robots
Paper and Code
Jul 11, 2022

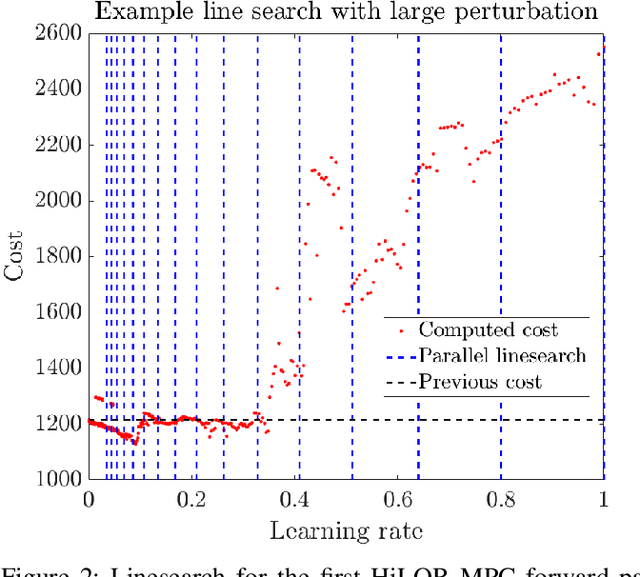
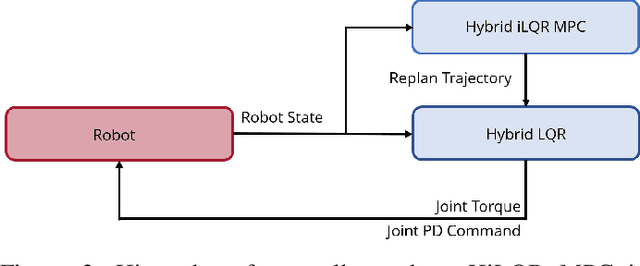
Model Predictive Control (MPC) is a popular strategy for controlling robots but is difficult for systems with contact due to the complex nature of hybrid dynamics. To implement MPC for systems with contact, dynamic models are often simplified or contact sequences fixed in time in order to plan trajectories efficiently. In this work, we extend Hybrid iterative Linear Quadratic Regulator to work in a MPC fashion (HiLQR MPC) by 1) modifying how the cost function is computed when contact modes do not align, 2) utilizing parallelizations when simulating rigid body dynamics, and 3) using efficient analytical derivative computations of the rigid body dynamics. The result is a system that can modify the contact sequence of the reference behavior and plan whole body motions cohesively -- which is crucial when dealing with large perturbations. HiLQR MPC is tested on two systems: first, the hybrid cost modification is validated on a simple actuated bouncing ball hybrid system. Then HiLQR MPC is compared against methods that utilize centroidal dynamic assumptions on a quadruped robot (Unitree A1). HiLQR MPC outperforms the centroidal methods in both simulation and hardware tests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge